Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. Aug 10, 2016; 7(15): 302-315
Published online Aug 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i15.302
Published online Aug 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i15.302
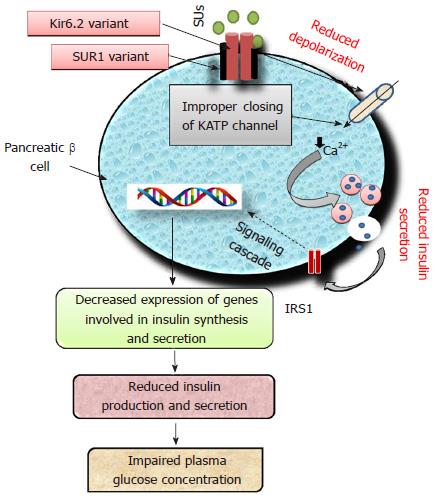
Figure 3 Schematic diagram showing the Kir6.
2 and SUR1 variants affecting sulfonylurea efficacy. Pancreatic β cell membrane with SUR1/Kir6.2 variant leads to improper closing of KATP channel on binding with SUs. This subsequently leads to poor membrane depolarization and less influx of Ca2+ ions which will result in less and delayed insulin secretion. Hence, low level of insulin molecules will be available to bind with IRS1 and lead to an impaired signaling cascade resulting in poor management of glycemic condition. SUs: Sulfonylureas; SUR1: Sulfonylurea receptor 1; KATP: ATP-sensitive potassium channel; IRS1: Insulin receptor substrate 1; SUR 1: Sulfonylurea Receptor 1.
- Citation: Singh S, Usman K, Banerjee M. Pharmacogenetic studies update in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(15): 302-315
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i15/302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i15.302