Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Dec 25, 2015; 6(18): 1345-1354
Published online Dec 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i18.1345
Published online Dec 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i18.1345
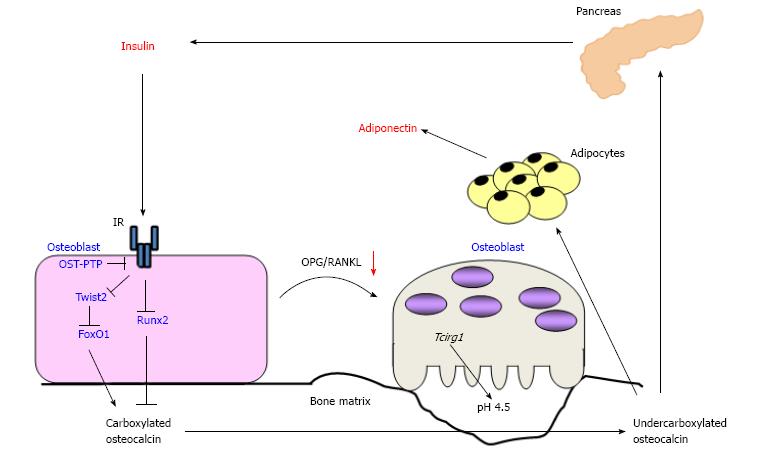
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the endocrine loops between bone and pancreas.
Insulin signaling stimulates the expression of osteocalcin and osteoblastic differentiation via inhibiting Twist2, an inhibitor of Runx2, as well as FoxO1, resulting in accumulation of carboxylated osteocalcin in bone matrix. Conversely, insulin activates osteoclasts and accelerate bone turnover via increasing the ratio of osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand. Activated osteoclasts decarboxylate bone matrix-embedded osteocalcin, and then undercarboxylated osteocalcin (ucOC) is released into the circulation. UcOC stimulates the expression of insulin in pancreas and of adiponectin in adipose tissue. OST-PTP: Osteotesticular protein tyrosine phosphatase; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; OPG/RANKL: Osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; IR: Insulin receptor.
- Citation: Kanazawa I. Osteocalcin as a hormone regulating glucose metabolism. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(18): 1345-1354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i18/1345.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i18.1345