Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Oct 25, 2015; 6(14): 1259-1273
Published online Oct 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i14.1259
Published online Oct 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i14.1259
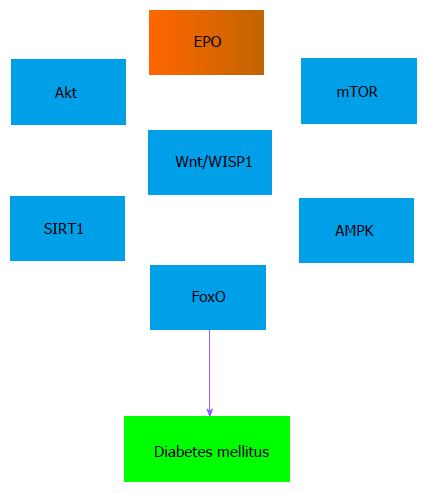
Figure 1 Erythropoietin signal transduction pathways that can lead to clinical benefit during diabetes mellitus.
EPO governs a number of signal transduction pathways that involve protein kinase B (Akt), the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), Wnt and WISP1 signaling, mammalian forkhead transcription factors of the O class (FoxO), silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) (SIRT1), and AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK). EPO: Erythropoietin; Akt: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; FoxO: Factors of the O class; SIRT1: Silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 (Saccharomyces cerevisiae); AMPK: AMP activated protein kinase.
- Citation: Maiese K. Erythropoietin and diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(14): 1259-1273
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i14/1259.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i14.1259