Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Sep 25, 2015; 6(12): 1223-1242
Published online Sep 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i12.1223
Published online Sep 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i12.1223
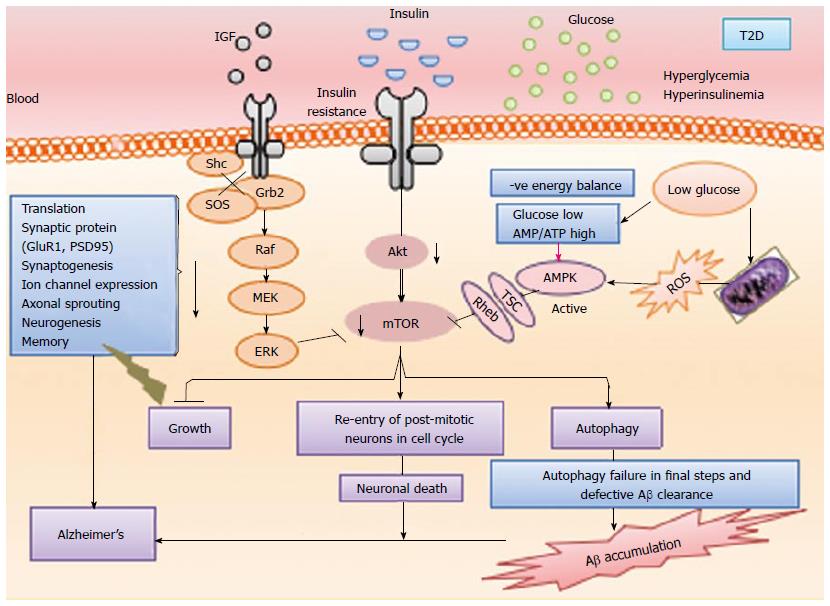
Figure 5 Diagrammatic representation of mammalian target of rapamycin pathway: A crucial intersection of type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
Diabetes results in dysfunctional insulin signaling which brings mTOR pathway down and ultimately results in autophagy failure to accumulate Aβ, inhibit re-entry of post mitotic neurons in cell cycle, stimulate aberrant growth pathways, lose of translational control and impaired neurogenesis, etc. T2D: Type 2 diabetes; IGF: Insulin like growth factor; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; Aβ: Amyloid beta; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Sandhir R, Gupta S. Molecular and biochemical trajectories from diabetes to Alzheimer’s disease: A critical appraisal. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(12): 1223-1242
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i12/1223.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i12.1223