Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Sep 25, 2015; 6(12): 1223-1242
Published online Sep 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i12.1223
Published online Sep 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i12.1223
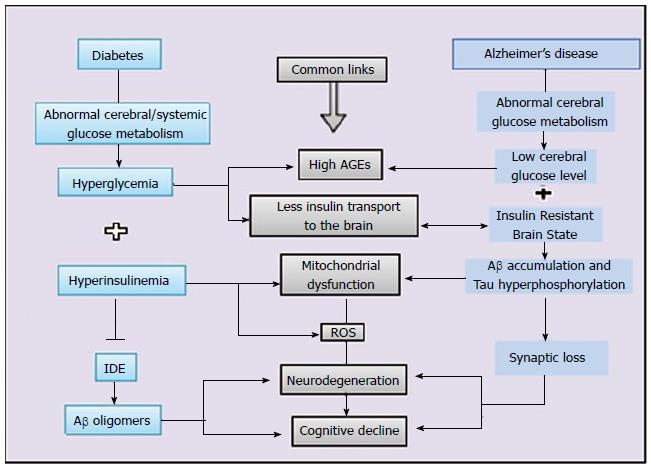
Figure 1 Schematic representation of commonalities between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
Hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia are hallmark features of diabetes which leads to advanced glycation end product, reduced insulin supply to brain as well as mitochondrial dysfunction, which further leads to vicious cycle of oxidative stress. On the other side, any defect in glucose metabolism and insulin signaling in brain is one metabolic status of Alzheimer’s disease brain which translates into insulin resistant brain status and converges to all common interfaces of mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and neurodegenrtaion. IDE: Insulin degrading enzyme; Aβ: Amyloid beta; AGEs: Advanced glycation end products; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Sandhir R, Gupta S. Molecular and biochemical trajectories from diabetes to Alzheimer’s disease: A critical appraisal. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(12): 1223-1242
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i12/1223.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i12.1223