Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2015; 6(1): 67-79
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.67
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.67
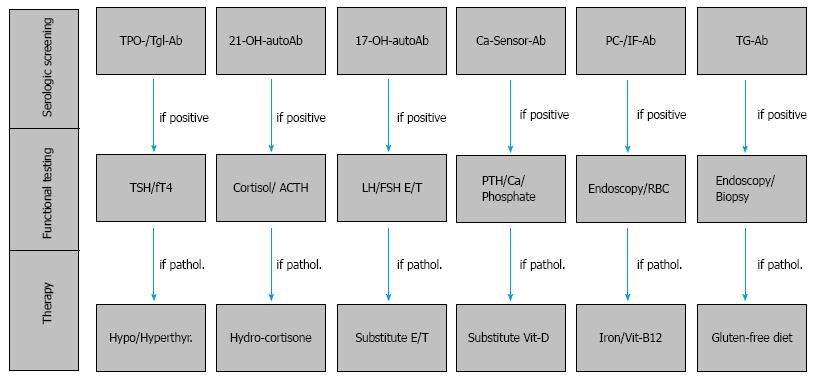
Figure 3 Serologic and functional screening in patients with type 1 diabetes.
The serologic and functional screening for associated autoimmune diseases in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) performed at the onset of T1D and during follow-up appointments every two years. After diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction, adrenal failure, primary hypogonadism, hypoparathyroidism, type A autoimmune gastritis with or without pernicious anemia and celiac disease, substitution proceeds with levothyroxine, hydrocortisone, estradiol or testosterone, vitamin D, iron tablets and vitamin B12 intramuscularly, with a strict gluten-free diet. In contrast, hyperthyroidism due to the autoimmune Graves’ disease will be managed first with the administration of anti-thyroid drugs (e.g., methimazole). Ab: Antibody; ACTH: Adrenocorticotropic hormone; Ca: Calcium; Ca-Sensor: Calcium-sensing receptor; E: Estradiol; FSH: Follicle-stimulating hormone; fT4: Free thyroxine; Hypo: Hypothyroidism; Hyperthyr: Hyperthyroidism; IF: Intrinsic factor; LH: Luteinizing hormone; PC: Parietal cell; PTH: Parathyroid hormone; RBC: Red blood cell count; T: Total testosterone; TG: Transglutaminase/deaminated anti-gliadin; Tgl: Thyroglobulin; TPO: Thyroid peroxidase; TSH: Thyrotropin; Vit: Vitamin; 17-OH: 17-hydroxylase; 21-OH: 21-hydroxylase.
- Citation: Hansen MP, Matheis N, Kahaly GJ. Type 1 diabetes and polyglandular autoimmune syndrome: A review. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(1): 67-79
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i1/67.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.67