Copyright
©The Author(s) 2014.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2015; 6(1): 109-124
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109
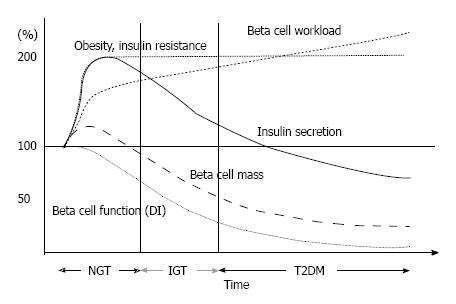
Figure 6 Hypothesis for change in β-cell function and mass during development of abnormal glucose tolerance.
The magnitude of the increased demand for insulin due to insulin resistance caused by excess caloric intake and physical inactivity exceeds the magnitude of β-cell mass expansion, resulting in an increase in β-cell workload. In individuals who are susceptible to type 2 diabetes (T2DM), increased β-cell workload may lead to β-cell failure and the development of T2DM. Adopted and modified from ref.[109].
- Citation: Saisho Y. β-cell dysfunction: Its critical role in prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(1): 109-124
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i1/109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109