Copyright
©The Author(s) 2014.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2015; 6(1): 109-124
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109
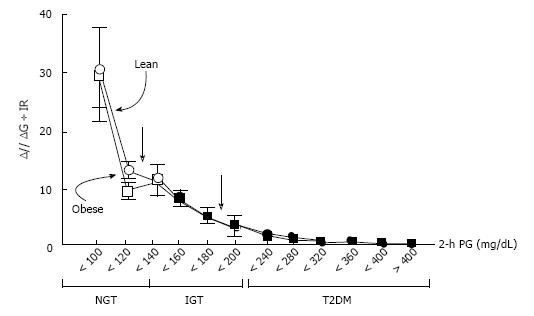
Figure 2 Insulin secretion/insulin resistance (disposition) index (I/G ÷ IR) during 75g-oral glucose tolerance test in individuals with normal glucose tolerance, impaired glucose tolerance, and type 2 diabetes as a function of the 2 h plasma glucose concentration in lean and obese subjects.
I/G: Insulinogenic index (Insulin 0-30 min/Glucose 0-30 min); IR: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance [HOMA-IR; fasting insulin (mU/L) x glucose (mmol/L)/22.5]. Adapted from ref.[9]. NGT: Normal glucose tolerance; IGT: Impaired glucose tolerance; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes; PG: Plasma glucose.
- Citation: Saisho Y. β-cell dysfunction: Its critical role in prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(1): 109-124
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i1/109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109