Copyright
©The Author(s) 2014.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2015; 6(1): 109-124
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109
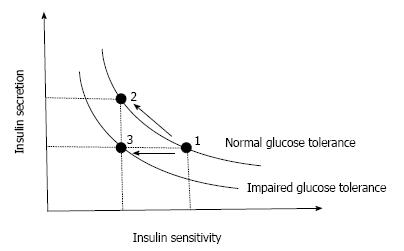
Figure 1 Insulin secretion-insulin sensitivity relationship.
In a physiological condition, when insulin sensitivity decreases, insulin secretion increases to maintain normoglycemia (1→2), showing a hyperbolic curve. When insulin secretion fails to compensate, the hyperbolic curve shifts to the left and abnormal glucose tolerance develops (1→3).
- Citation: Saisho Y. β-cell dysfunction: Its critical role in prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(1): 109-124
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i1/109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109