Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2014; 5(5): 666-677
Published online Oct 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.666
Published online Oct 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.666
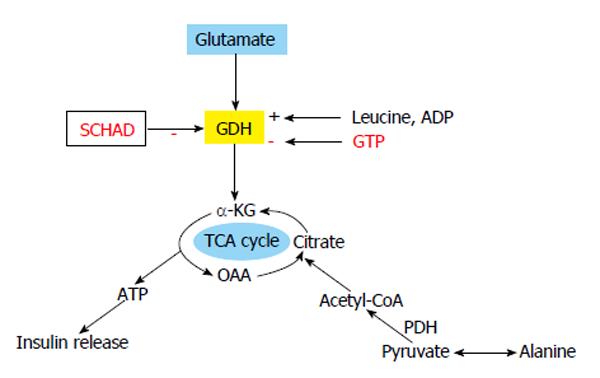
Figure 3 Glutamate and alanine as insulin secretagogues.
Protein induced hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia due to loss of function mutation in HADH gene (SCHAD). Alanine is deaminated to pyruvate and pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) converts it to acetyl CoA, which can enter TCA cycle to generate ATP for closing KATP channel. TCA: Tricarboxylic acid cycle; α-KG: Alpha ketoglutarate; GDH: Glutamate dehydrogenase; OAA: Oxaloacetic acid.
- Citation: Chandran S, Yap F, Hussain K. Molecular mechanisms of protein induced hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. World J Diabetes 2014; 5(5): 666-677
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v5/i5/666.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.666