Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2014; 5(5): 666-677
Published online Oct 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.666
Published online Oct 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.666
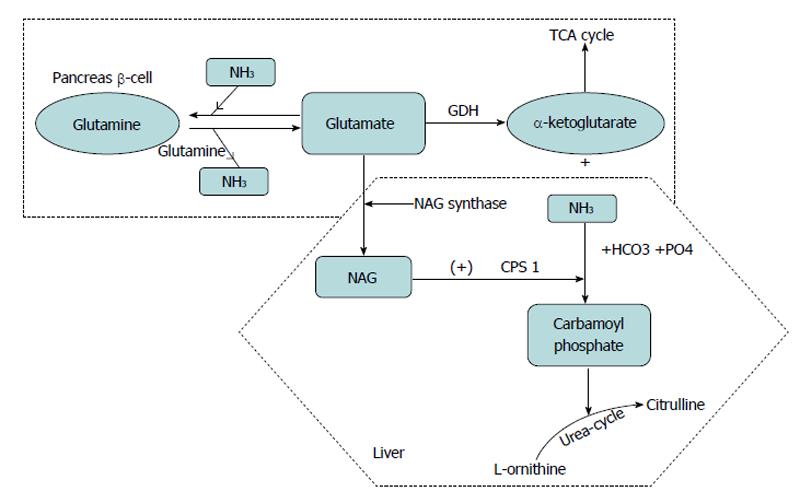
Figure 2 Glutamate metabolism.
Oxidation of glutamate by glutamate dehydrogenase liberates free ammonia (NH3) and alpha ketoglutarate, which enters tricarboxylic acid cycle cycle and generates ATP. In the liver glutamate also generates N-acetylglutamate (NAG), which in turn allosterically activates carbomyl phosphate synthetase (CPS) to regulate ammonia detoxification into urea. Glutamine provides a substrate for ammonia buffering, by adding ammonia to glutamate to form glutamine. TCA: Tricarboxylic acid cycle; GDH: Glutamate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Chandran S, Yap F, Hussain K. Molecular mechanisms of protein induced hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. World J Diabetes 2014; 5(5): 666-677
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v5/i5/666.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.666