Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2014; 5(4): 444-470
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i4.444
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i4.444
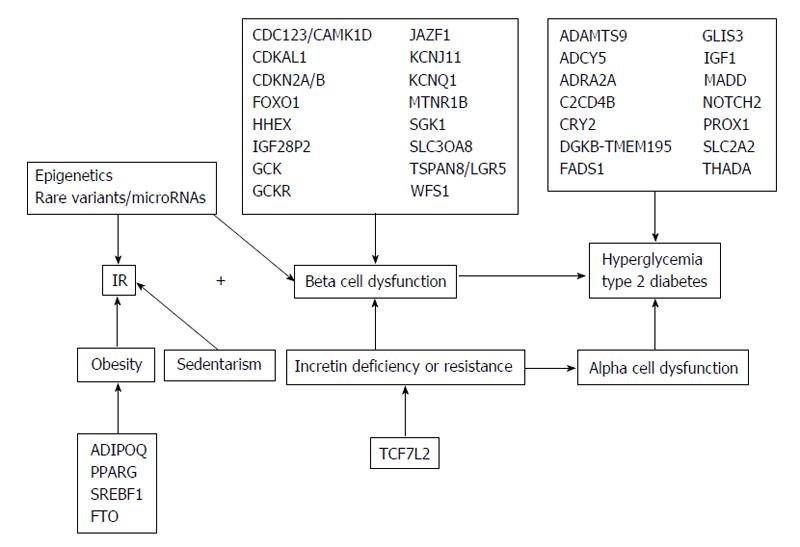
Figure 3 Possible mechanisms of confirmed and potential risk single-nucleotide poly morphisms in type 2 diabetes.
Many single-nucleotide poly morphisms (SNPs) affect pancreatic beta-cell function. Gene symbols represent SNPs in or near these gene loci. Likely epigenetic alterations microRNAs and/or rare genetic variants also have a critical role. The mechanisms by which some genes increase the risk of diabetes are not yet know. CDC123: Cell division cycle 123; CAMK1D: Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 1D; CDKAL1: CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1-like 1; CDKN2A/B: Distal to the genes cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors 2A; FOXO1: Fork head box protein O1; HHEX: IDE-near hematopoietically expressed home box and insulin degrading enzyme; IGF2BP2: IGF2 mRNA binding protein 2; GCK: Glucokinase; GCKR: Glucokinase regulator; JAZF1: Juxtaposed with another zinc kinger protein 1; KCNJ11: Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 11; KCNQ1: Potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 1; MTNR1B: Melatonin receptor 1B; SGK1: Serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1; SLC30A8: Solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter) member A8; TSPAN8: Tetraspanin 8; LGR5: Leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5; WFS1: Wolfram syndrome 1; ADAMTS9: Disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 9; ADCY5: Adenylate cyclase 5; ADRA2A: Adrenergic, alpha-2A-, receptor; C2CD4B: C2 calcium-dependent domain containing 4B; CRY2: Cryptochrome 2; DGKB: Diacylglycerol kinase beta 90 kDa; TMEM195: Transmembrane protein 195; FADS1: Fatty acid desaturase 1; GLIS3: GLIS family zinc finger 3; IGF1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; MADD: MAP kinase-activating death domain; NOTCH2: Notch homolog protein 2; PROX1: Prospero-homebox 1; SLC2A2: Solute carrier family 2, member A2; THADA: Thyroid adenoma associated; ADIPO: Adiponectin; PPARG: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma; SREBF1: Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1; FTO: Fat mass and obesity-associated; TCF7L2: Transcription factor 7-like 2; IR: Insulin resistance.
- Citation: Martín-Timón I, Sevillano-Collantes C, Segura-Galindo A, Cañizo-Gómez FJD. Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Have all risk factors the same strength? World J Diabetes 2014; 5(4): 444-470
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v5/i4/444.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v5.i4.444