Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2013; 4(4): 135-144
Published online Aug 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.135
Published online Aug 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.135
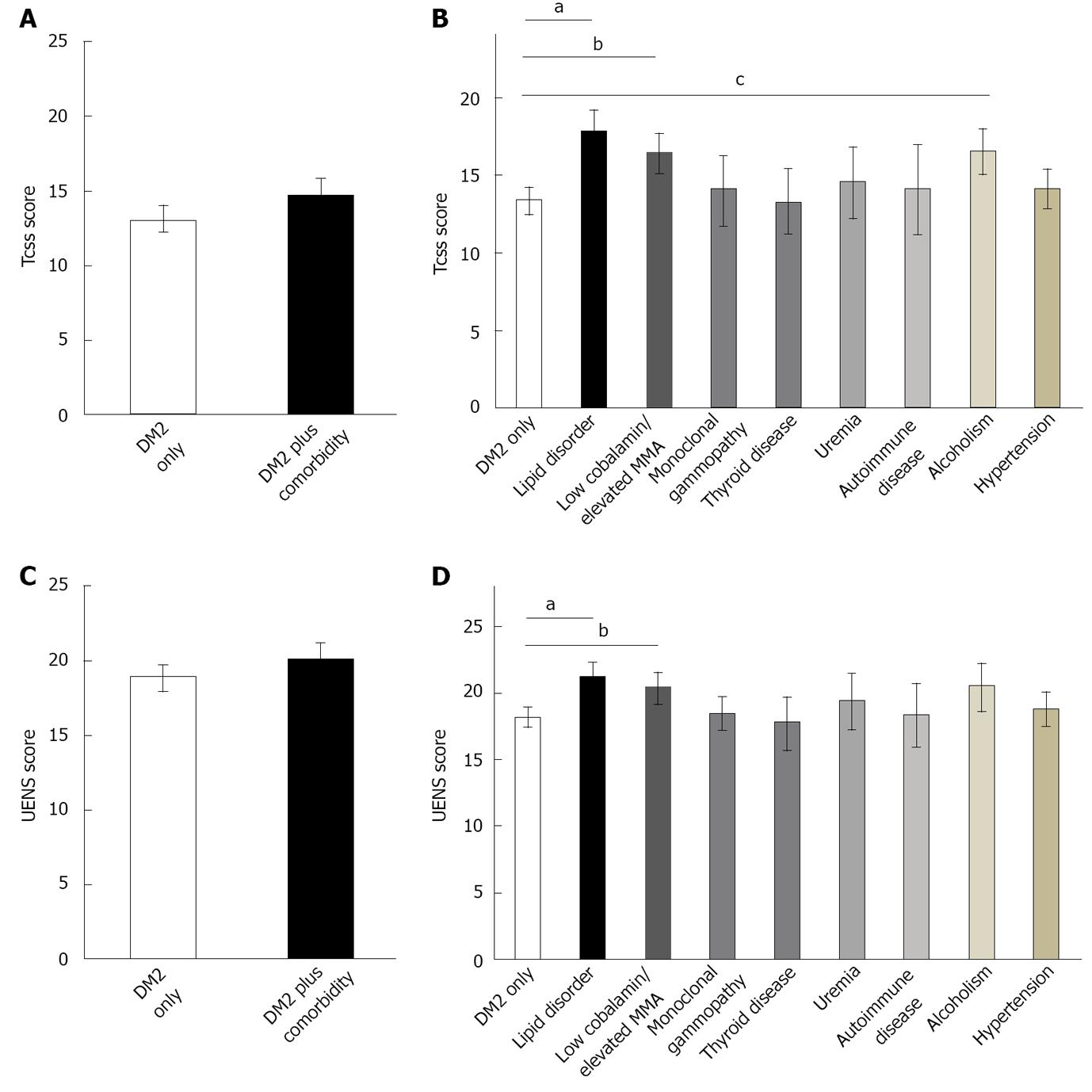
Figure 2 In type 2 diabetes subjects.
A, B: Peripheral neuropathy (PN) severity was assessed using the Toronto Clinical Scoring System (TCSS); C, D: The Utah Early Neuropathy Scale (UENS) for patients without (DM2 Only) and with (DM2 Plus Comorbidity) comorbidities capable of contributing to PN. As with type 1 diabetes, there was no significant difference between cohorts for either TCSS (A) or UENS (C) values. When subcategorized by specific comorbidity, however, patients with type 2 diabetes having a concomitant lipid disorder, cobalamin deficiency or elevated fasting methylmalonic acid level, or alcoholism had greater TCSS (B) scores when compared to DM2 only subjects. Using UENS values (D), presence of a lipid disorder or cobalamin deficiency/elevated fasting methylmalonic acid level was associated with greater PN severity. Other examined comorbidities were not associated with greater severity of PN when compared to DM2 only subjects. The presence of significant differences between the subcohorts with comorbidities and DM2 only cohort are indicated with(aP < 0.007 vs lipid disorder, ANOVA), (bP < 0.007 vs low cobalamin or elevated fasting methylmalonic acid level, ANOVA), and (cP < 0.007 vs alcoholism, ANOVA).
- Citation: Sachedina S, Toth C. Association of comorbidities with increasing severity of peripheral neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2013; 4(4): 135-144
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v4/i4/135.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.135