Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2013; 4(4): 101-113
Published online Aug 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.101
Published online Aug 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.101
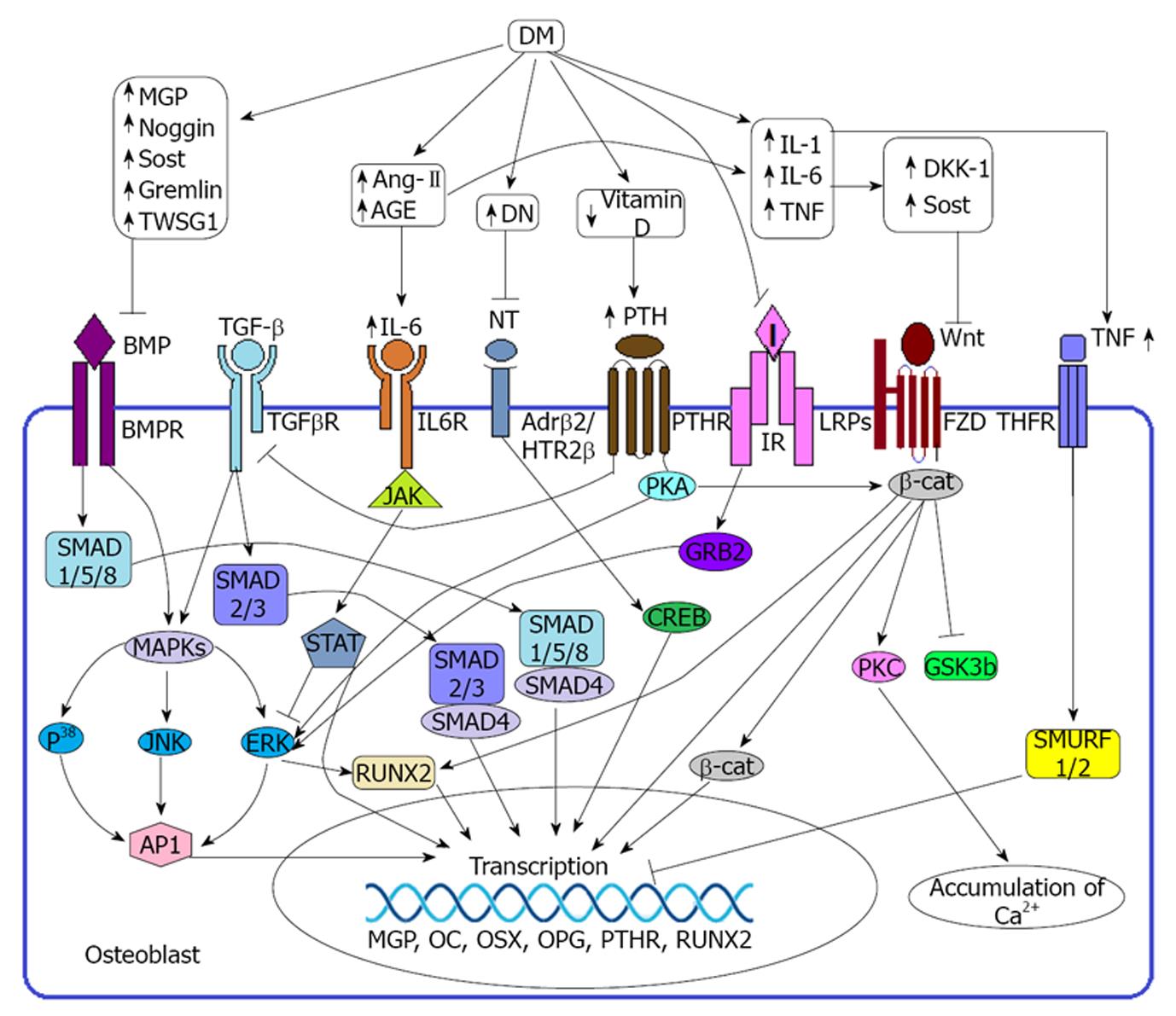
Figure 1 Diabetes mellitus induced regulation of osteoblast.
Duringhealthy condition bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), Wnt, insulin and neurotransmitter signaling are mandatory to the osteoblast for its normal functioning and survival. Binding of BMP with its receptor (BMPR) activates the corresponding gene through (a) Smad depended pathway: which requires the SMADs protein (SMAD 1/5/8) or (b) non smad depended pathway: in which activates RUNX2 or AP-1 through MAPK-ERK mediated pathway. Wnt-Frizzled pathway positively regulates gene expression through β-catenin or RUNX2 mediated pathway and Calcium accumulation through PKC mediated pathway. TGF-β is also a positive regulator of osteoblast function and exerts its effect on the respective gene through SMAD 2/3 depended pathway or MAPK-ERK mediated pathway. Peripheral nerve exposure to the osteoblast signals through the adrenergic receptor 2 β (Adrβ2) or 5HTR induced pathway. Binding of neurotransmitters on the Adrβ2 or 5HTR receptor activates ERK or CREB to induce the expression of osteoblastic gene. Insulin is a beneficial factor of bone formation and it exerts its effect through GRB2-ERK mediated pathway. During diabetes mellitus (DM), hyperglycemia may induce the expression of several BMP inhibitors including MGP, Noggin, Sost, Gremlin, TWSG1 as well as several Wnt inhibitors including DKK-1, Sost. DM also induces the production of different proinflammatory cytokines including interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-1, AT-2 and TNF which negatively regulates osteoblast functioning. Binding of IL-6 with its receptor IL-6 receptor (IL6R) sequesters ERK pathway as well as induce the gene to transcribe several inhibitors including MGP, OPG OSX. DM induced DN limits the nerve signaling through damaging the peripheral nerves. TNF binding with TNFR induce SMURF1/2 and thereby inhibit the transcription process. DM also reduces the production of vitamin D which in turn induces the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH binding with PTH receptor (PTHR) inhibits TGF-β signaling through inhibiting TGFβ receptor (TGFβR) although PTHR activates β-Cat and ERK pathways. DM induced IR (type-2DM) or insulin deficiency (Type-1DM) also limits insulin mediated bone formation. TNT: Neurotransmitter; HTR2β: 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2 β; I: Insulin; IR: Insulin receptor; LRP: Low density lipoprotein receptor related protein; FZD: Frizzled; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFR: TNF receptor; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: Signal transducers and activators of transcription; AP-1: Activator protein 1; ERK: Extracellular signal regulated kinase; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; RUNX2: Runt related transcription factor 2; PKA: Protein kinase A; PKA: Protein kinase C; β-cat: β catenin; GSK3b: Glycogen synthase kinase 3b; SMURF: SMAD ubiquitylation regulatory factor; MGP: Matrix gla protein; OC: Osteocalcin; OSX: Osterix; OPG: Osteoprotegerin; DKK-1: Dickkopf related protein 1; Sost: Sclerostin; TWSG1: Twisted gremlin; Ang-II: Angiotensin-II; AGE: Advance glycation end product; GRB2: Growth factor receptor bound protein.
- Citation: Roy B. Biomolecular basis of the role of diabetes mellitus in osteoporosis and bone fractures. World J Diabetes 2013; 4(4): 101-113
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v4/i4/101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.101