Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2013; 4(3): 70-75
Published online Jun 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i3.70
Published online Jun 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i3.70
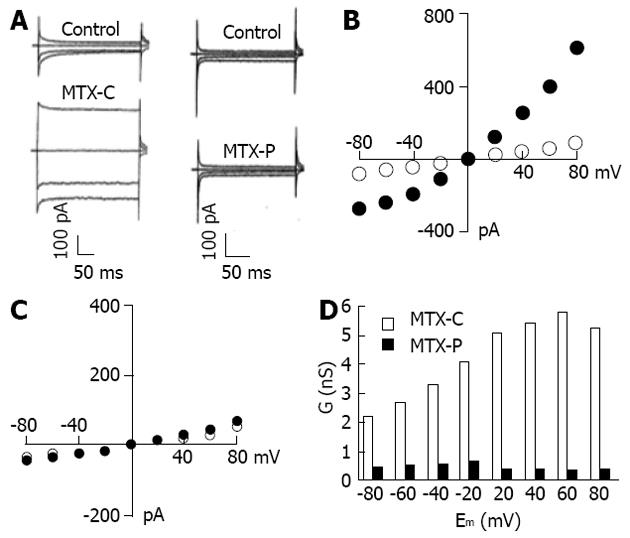
Figure 4 Non-voltage activated cation current induced by caribbean maitotoxin or pacific maitotoxin in the calcium free extracellular solution.
A: Current traces measured before and after caribbean maitotoxin (MTX-C) or pacific maitotoxin (MTX-P) administration at -80, -40, 0 and 40 mV when held at 0 mV; B and C: I-V relationships of MTX-C (B) and MTX-P (C) elicited currents. The solid circles represent current amplitudes measured after MTX-C (B) or MTX-P (C) administration. The open circles represent the current recorded under the control condition; D: Current conductance measured at different test potentials in cells treated with MTX-C or MTX-P.
- Citation: Lu XZ, Deckey R, Jiao GL, Ren HF, Li M. Caribbean maitotoxin elevates [Ca2+]i and activates non-selective cation channels in HIT-T15 cells. World J Diabetes 2013; 4(3): 70-75
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v4/i3/70.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v4.i3.70