Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2012; 3(3): 38-53
Published online Mar 15, 2012. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v3.i3.38
Published online Mar 15, 2012. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v3.i3.38
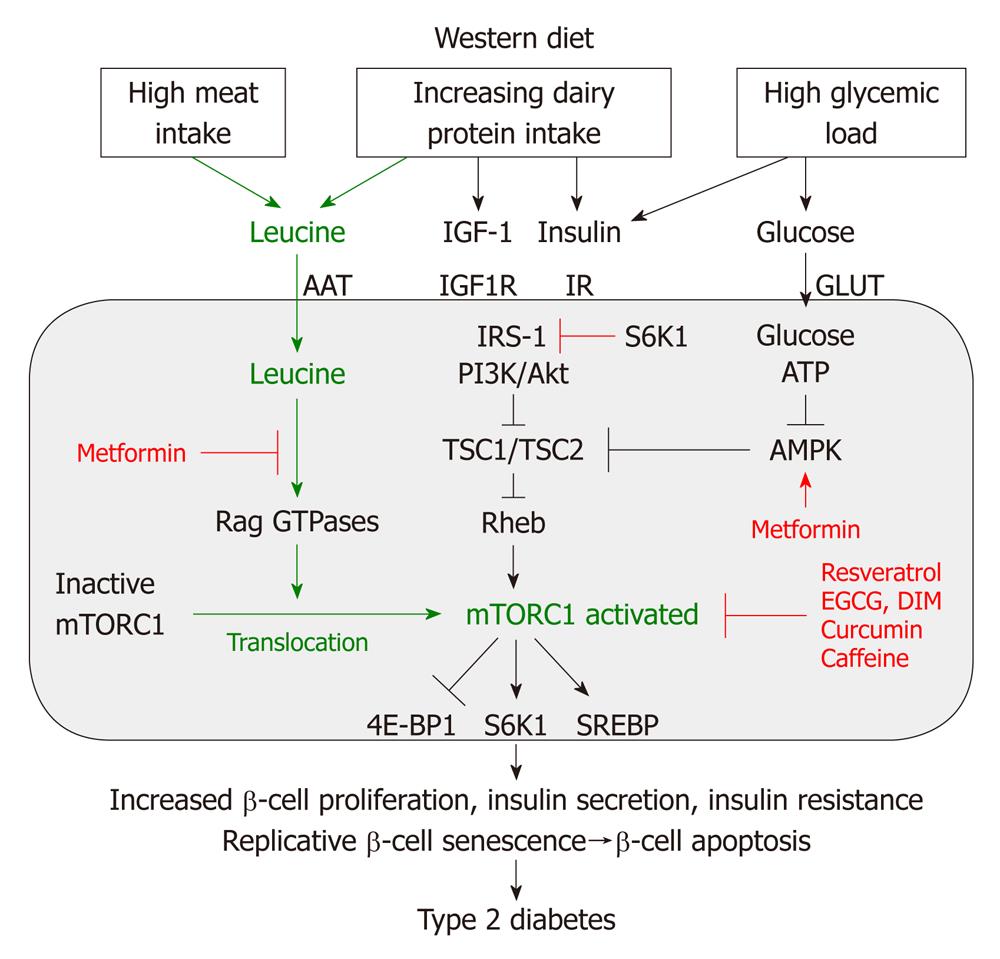
Figure 4 Nutrient-mediated over-stimulation of mTORC1 by leucine-enriched Western diet.
Leucine, insulin/insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and glucose activate mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Activated mTORC1 stimulates β-cell proliferation, increases insulin secretion and p70 S6 kinase 1 (S6K1)-mediated insulin resistance leading to early replicative β-cell senescence and apoptosis thus promoting the development of type 2 diabetes. AAT: Amino acid transporter; IR: Insulin receptor; GLUT: Glucose transporter protein; IRS-1: Insulin receptor substrate 1; PI3K: Phosphoinositol-3 kinase; Akt: Akt kinase [= protein kinase B (PKB)]; TSC1: Tuberous sclerosis complex 1 (hamartin); TSC2: Tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (tuberin); AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; EGCG: Epigallocatechin gallate; DIM: 3,3’-diindolylmethane; SREBP: Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor.
- Citation: Melnik BC. Leucine signaling in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes and obesity. World J Diabetes 2012; 3(3): 38-53
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v3/i3/38.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v3.i3.38