Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 102994
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.102994
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.102994
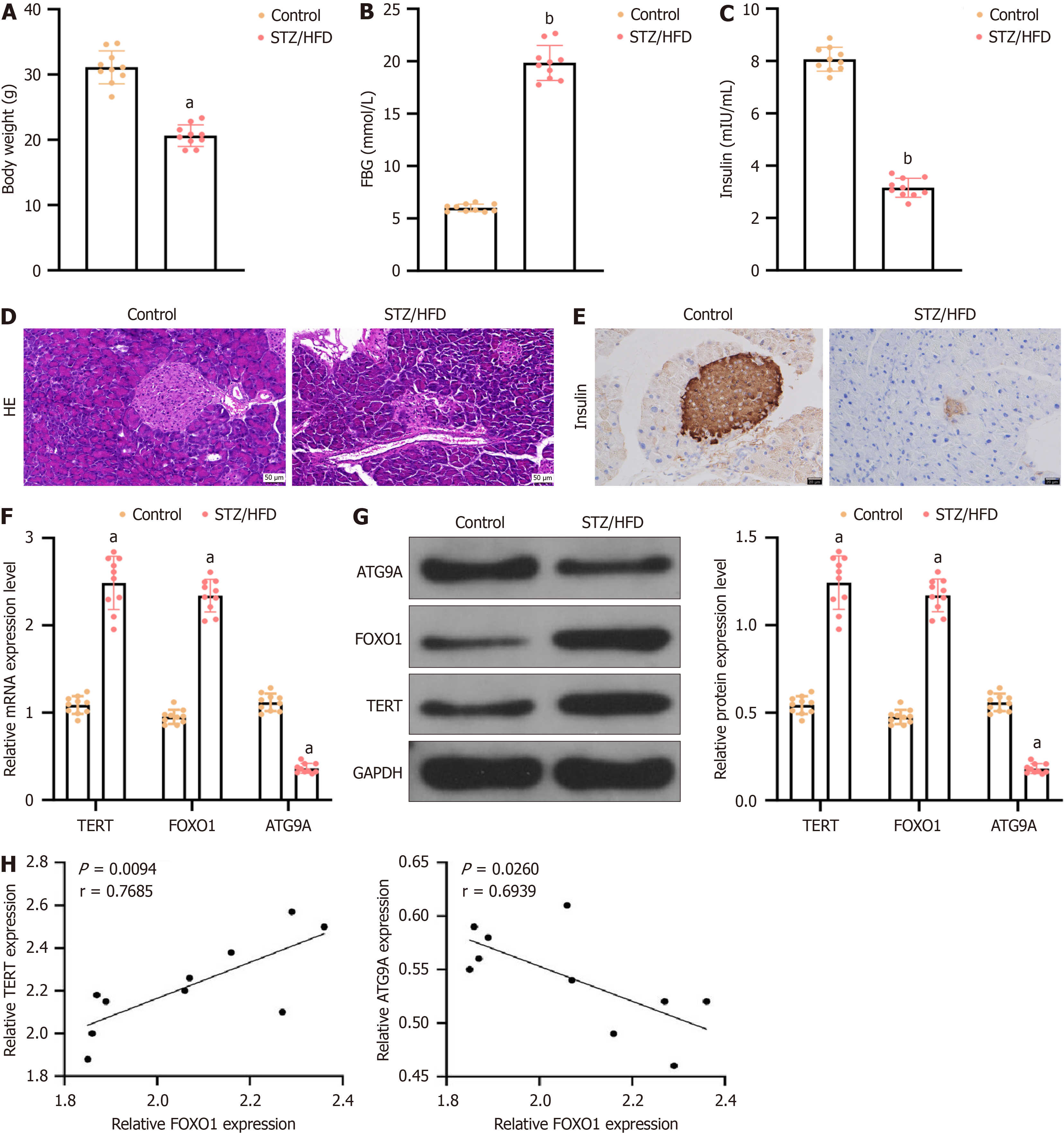
Figure 1 Altered expression of TERT, FOXO1 and ATG9A was found in the pancreatic tissues of type 2 diabetes mellitus model mice.
A type 2 diabetes mellitus model was generated by feeding mice a high-fat diet and administering intraperitoneal injections of streptozotocin. A and B: Mouse body weight and fasting blood glucose; C: Plasma insulin levels were measured using ELISAs; D: H&E staining was used to assess morphological changes in islet tissues (× 200); E: Immunohistochemistry was used to assess changes in insulin levels(× 400); F and G: TERT, FOXO1 and ATG9A mRNA and protein expression levels were analyzed via reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting; H: Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine the correlations among TERT, FOXO1 and ATG9A. The data are expressed as mean ± SD. n = 10 for in vivo experiments. aP < 0.05 vs control group, bP < 0.01 vs control group. FBG: Fasting blood glucose; HFD: High-fat diet; STZ: Streptozotocin.
- Citation: Lei XT, Chen XF, Qiu S, Tang JY, Geng S, Yang GY, Wu QN. TERT/FOXO1 signaling promotes islet β-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus by regulating ATG9A-mediated autophagy. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 102994
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/102994.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.102994