Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
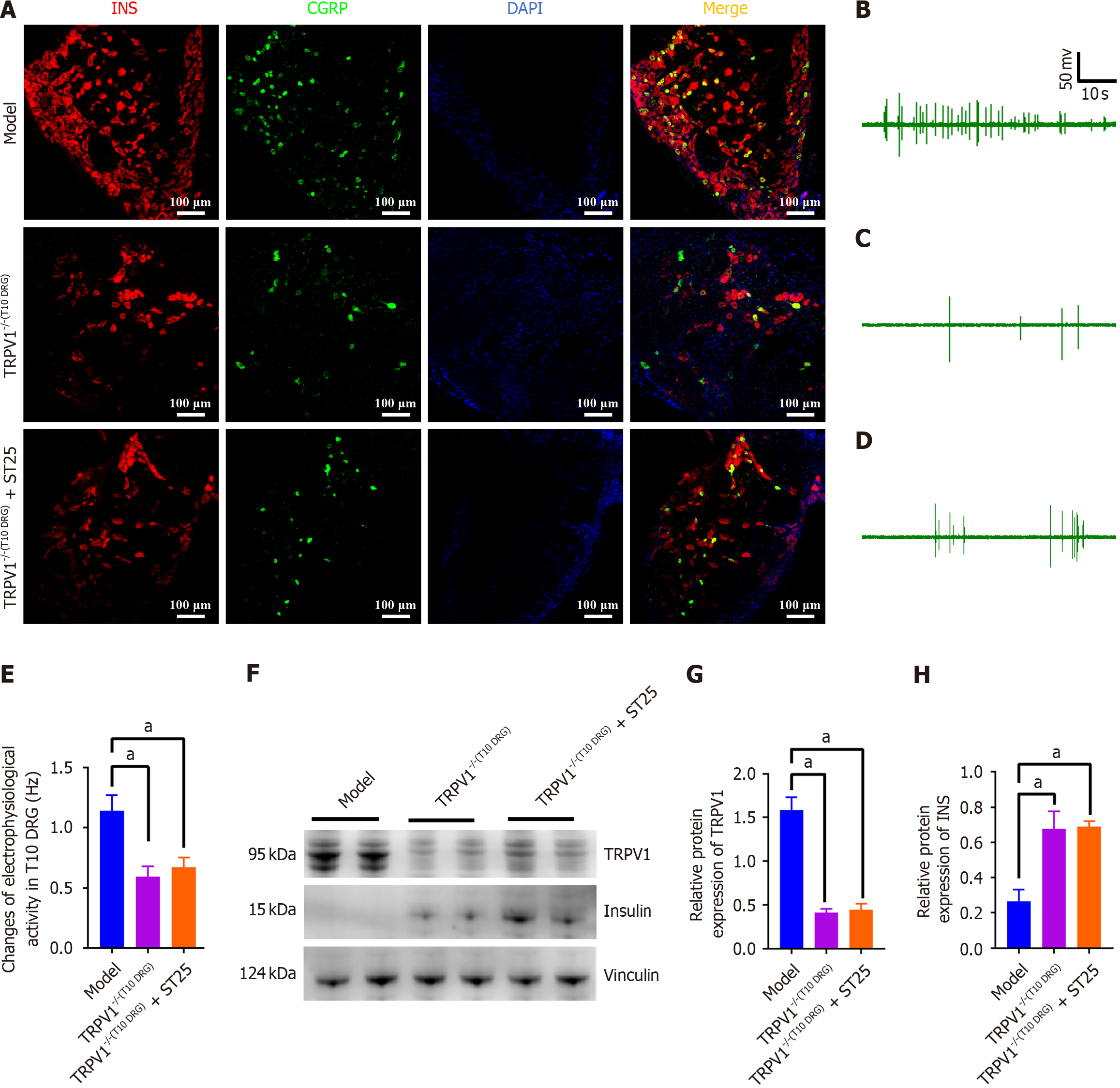
Figure 5 Modulation of pancreatic function by TRPV1 neuronal pathways in electroacupuncture-treated t10 dorsal root ganglion.
A: Representative immunofluorescence images illustrating co-expression of insulin (INS) and CGRP in the pancreas at 200 × magnification. Nuclei are stained blue with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, with red representing INS and green representing CGRP immunofluorescence; B-D: Electrophysiological activity measurements of the T10 DRG in model mice under different conditions: Untreated model, TRPV1 knockout (TRPV1-/-) in T10 DRG, and TRPV1-/- in T10 DRG followed by electroacupuncture (EA) at the ST25 acupoint; E: Discharge frequency associated with the groups mentioned in B-D; F-H: Impact of EA on the expression levels of TRPV1 and INS in the pancreas following capsazepine injection into the T10 DRG. GAPDH served as an internal reference protein. aP < 0.05 compared to the model or another treatment group. INS: Insulin; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; ST25: Tianshu acupoint.
- Citation: Liu Y, Yu Z, Wang X, Yuan MQ, Lu MJ, Gong MR, Li Q, Xia YB, Yang GH, Xu B, Litscher G, Xu TC. Neurophysiological mechanisms of electroacupuncture in regulating pancreatic function and adipose tissue expansion. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 101354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/101354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354