Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
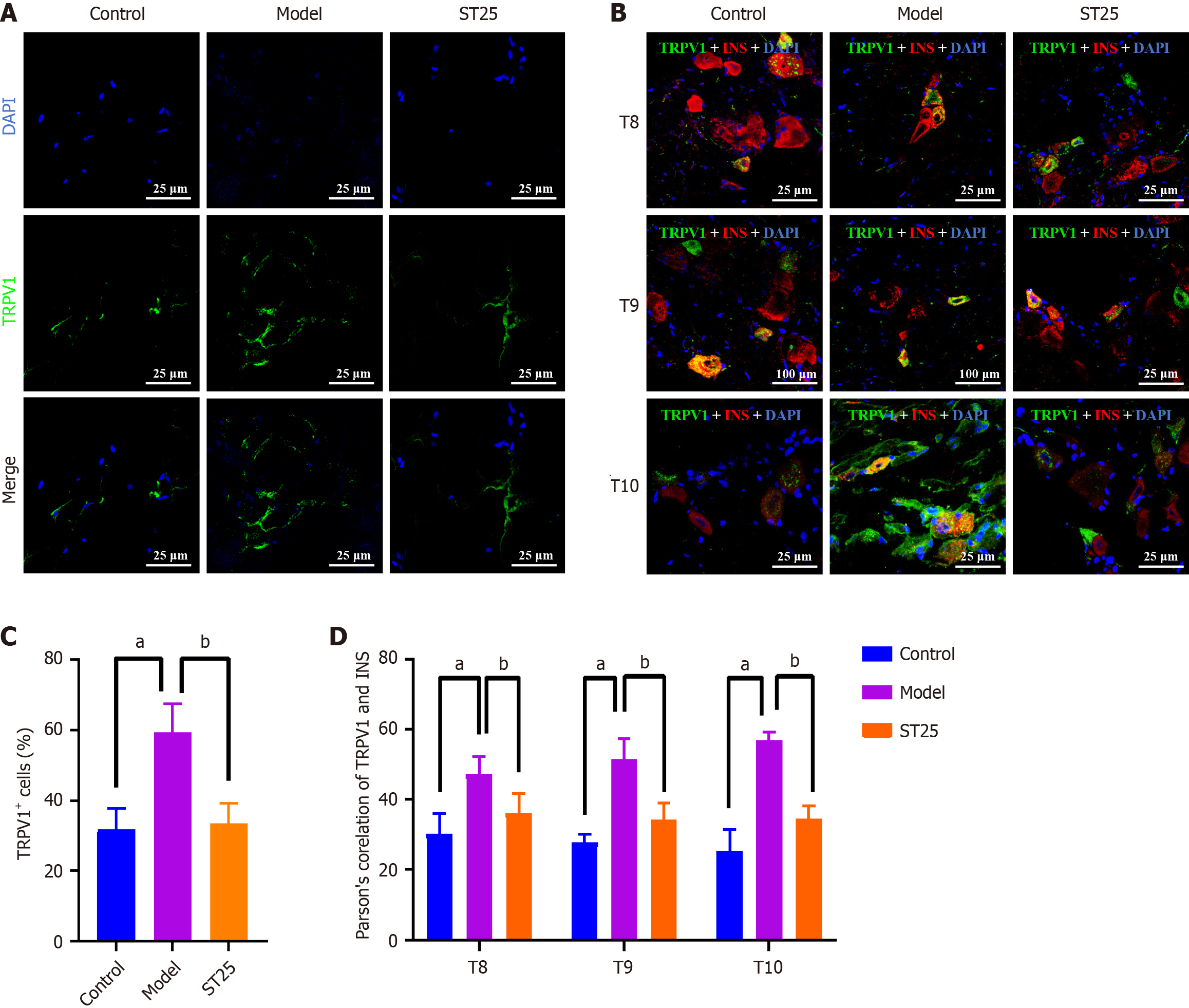
Figure 4 TRPV1-mediated enhancement of metabolic function by electroacupuncture.
A: Representative immunofluorescence images of pancreatic tissue across experimental groups. The nuclei are visualized in blue by 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), with green immunofluorescence indicating the presence of TRPV1. Islets were examined at 630 × magnification. A uniform scale bar of 25 μm applies to all groups; B: Representative immunofluorescenc images of the dorsal root ganglion across groups. Nuclei are stained blue by DAPI, with green immunofluorescence representing TRPV1 and red immunofluorescence representing insulin; C: Percentage of pancreatic TRPV1+ nerve fibers in each group; D: Illustrative immunofluorescence images showing co-expression of TRPV1 and INS in all groups. aP < 0.05 compared to the normal control group; bP < 0.05 compared to the model group. TRPV1: Transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily member 1; INS: Insulin; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Liu Y, Yu Z, Wang X, Yuan MQ, Lu MJ, Gong MR, Li Q, Xia YB, Yang GH, Xu B, Litscher G, Xu TC. Neurophysiological mechanisms of electroacupuncture in regulating pancreatic function and adipose tissue expansion. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 101354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/101354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354