Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
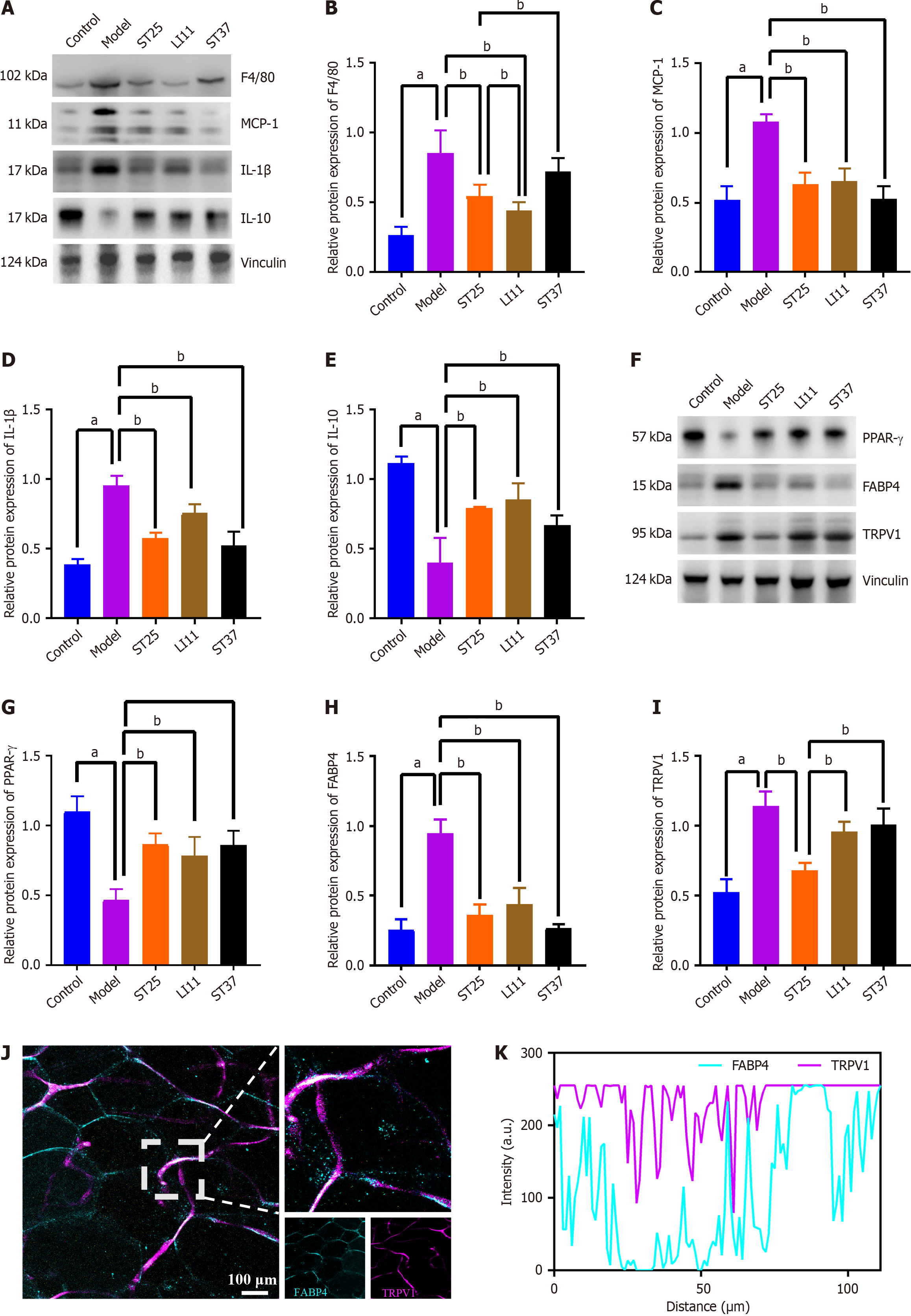
Figure 2 Electroacupuncture modulates inflammatory mediators in peripancreatic adipose tissue, enhancing metabolic function.
A and B: Electroacupuncture (EA)'s impact on the expression of F4/80 (also known as EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 1); A and C: Influence of EA on MCP-1 levels; A and D: Changes in interleukin (IL)-1β expression due to EA treatment; A and E: EA's effect on IL-10 expression; F and G: Expression levels of PPAR-γ following EA intervention; F and H: Adipose tissue expression of FABP4 in response to EA; F and I: TRPV1 expression in PAT after EA treatment. Vinculin served as a loading control; J: Representative immunofluorescence images of co-expression of FABP4 and TRPV1 in the pancreas of the model group (200 × magnification). Blue fluorescence representing FABP4, and TRPV1 is represented by purple fluorescence; K: Quantitative analysis of the co-localization of FABP4 and TRPV1 immunofluorescence, indicating a correlation between the two proteins. aP < 0.05 compared to the normal control group; bP < 0.05 compared to the model or another treatment group.
- Citation: Liu Y, Yu Z, Wang X, Yuan MQ, Lu MJ, Gong MR, Li Q, Xia YB, Yang GH, Xu B, Litscher G, Xu TC. Neurophysiological mechanisms of electroacupuncture in regulating pancreatic function and adipose tissue expansion. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 101354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/101354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354