Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
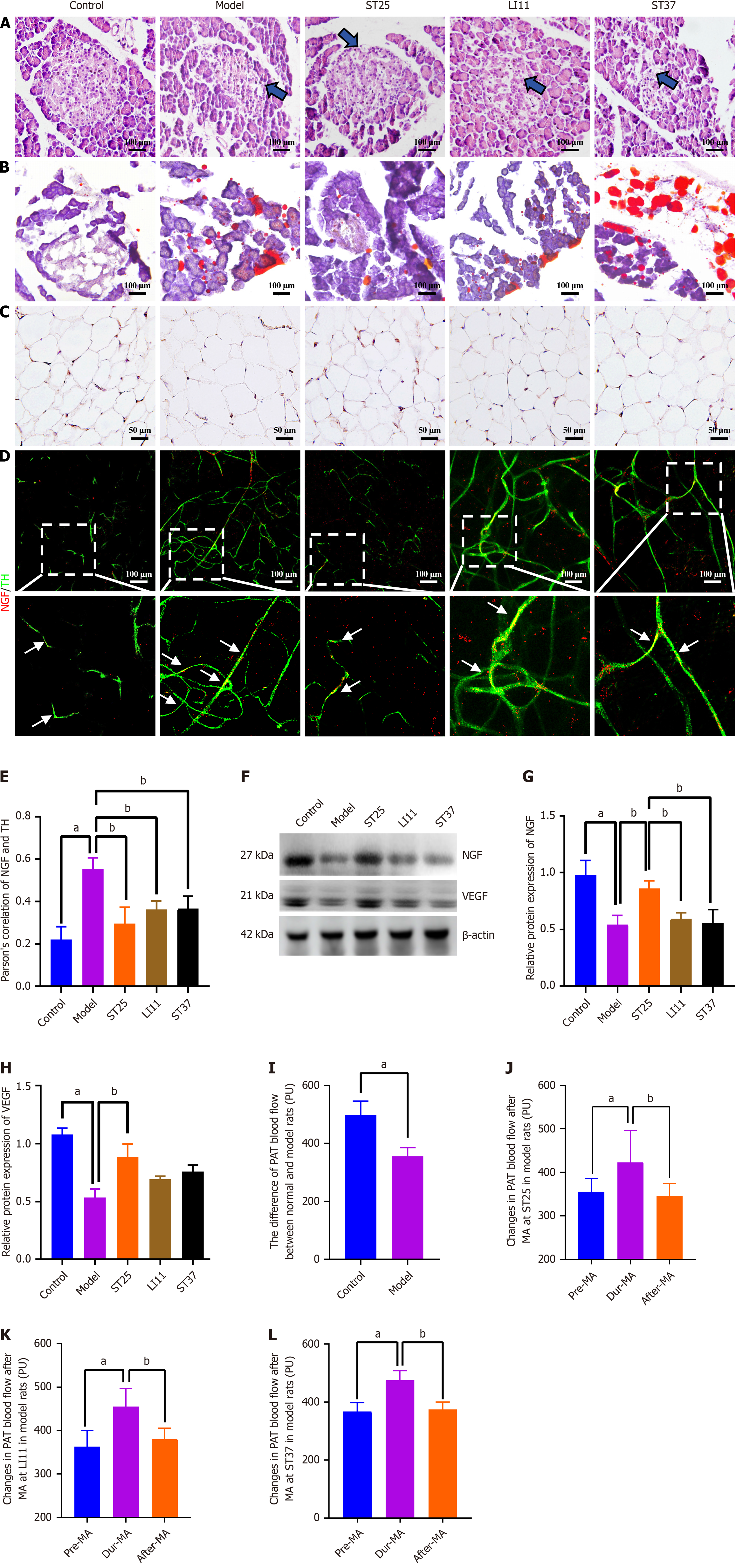
Figure 1 Electroacupuncture modulates the trophic influence of peripancreatic adipose tissue on the pancreatic intrinsic nervous system.
A: Histological alterations in pancreatic tissue and ectopic fat deposition in the pancreas across experimental groups (200 × magnification). Blue arrows indicate vacuolar-like changes; B: Comparative analysis of peripancreatic adipose tissue (PAT) blood perfusion between the control and model groups; C: Immunohistochemical staining for NGF in PAT under high magnification for the different groups (400 × magnification). Scale bar represents 50 μm; D: Illustrative immunofluorescence images showing co-expression of NGF and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in all groups (200 × magnification). Red fluorescence denotes NGF, while green fluorescence indicates TH. A uniform scale bar is applied to all groups; D: Pearson correlation analysis between NGF and TH expression (n = 5); E: Illustrative immunofluorescence images showing co-expression of NGF and TH in all groups (200 × magnification); F and G: Representative Western blot bands for NGF; F and H: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in PAT. Vinculin served as a loading control; I-L: PAT blood flow changes during electroacupuncture stimulation at acupoints ST25, LI11, and ST37 in normal rats, respectively. aP < 0.05 compared to the normal control group; bP < 0.05 compared to the model or alternative treatment group. TH: Tyrosine hydroxylase; ST25: Tianshu acupoint; LI11: Quchi acupoint; ST37: Shangjuxu acupoint.
- Citation: Liu Y, Yu Z, Wang X, Yuan MQ, Lu MJ, Gong MR, Li Q, Xia YB, Yang GH, Xu B, Litscher G, Xu TC. Neurophysiological mechanisms of electroacupuncture in regulating pancreatic function and adipose tissue expansion. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 101354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/101354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354