Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 98995
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.98995
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.98995
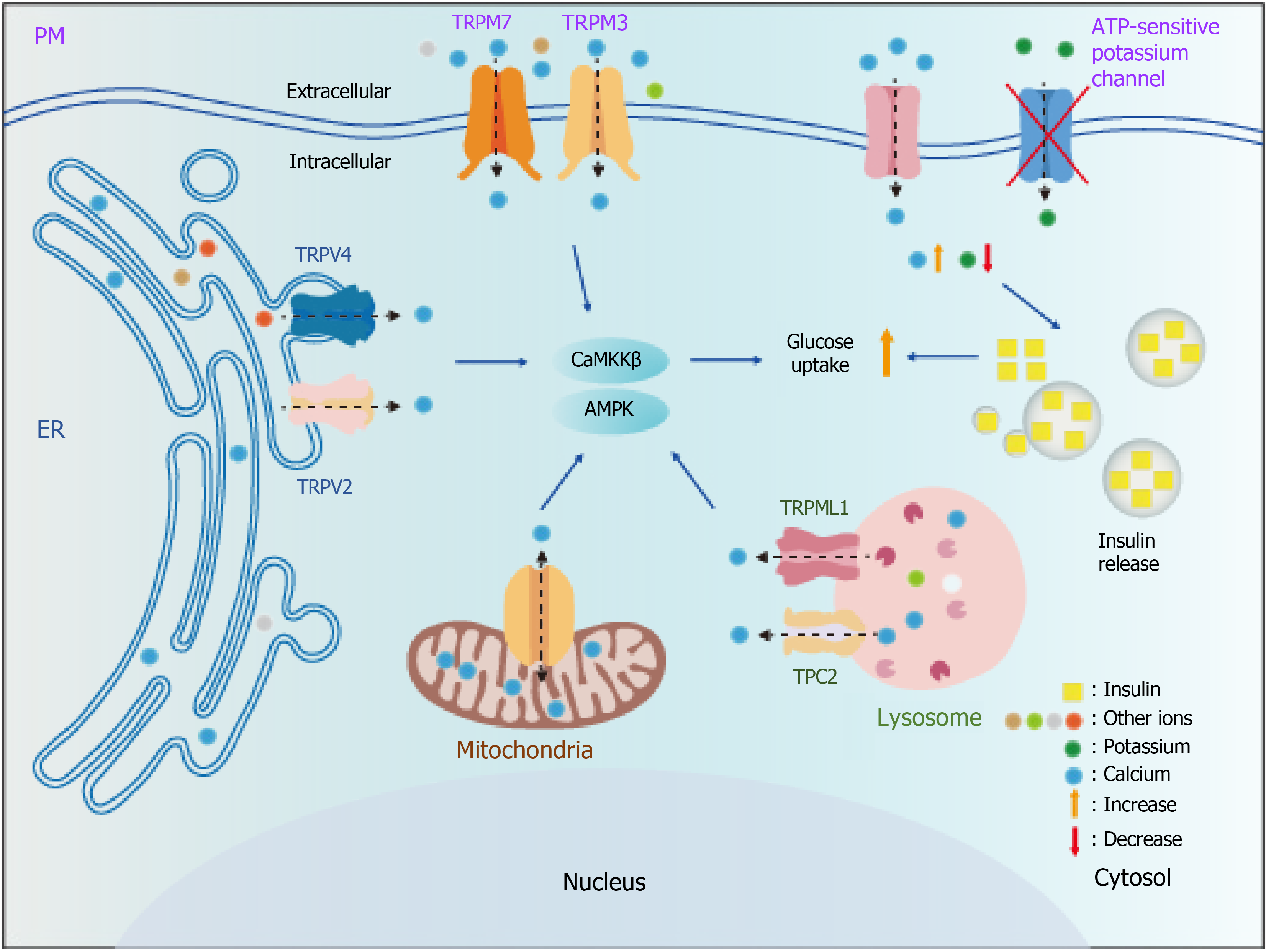
Figure 2 Potential roles of calcium-permeable ion channels in glucose uptake.
A working model to illustrate the possible role of calcium ion channels in glucose uptake. Various calcium ion channels located on various organelles and the plasma membrane can increase the cytosolic calcium release, then activating calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 2/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway via phosphorylation of the Thr172 site and leads to increased glucose uptake, thus treating type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Specific agonists could be potential therapeutic drugs for T2DM. PM: Plasma membrane; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum.
- Citation: Zhu JX, Pan ZN, Li D. Intracellular calcium channels: Potential targets for type 2 diabetes mellitus? World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 98995
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/98995.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.98995