Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 98995
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.98995
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.98995
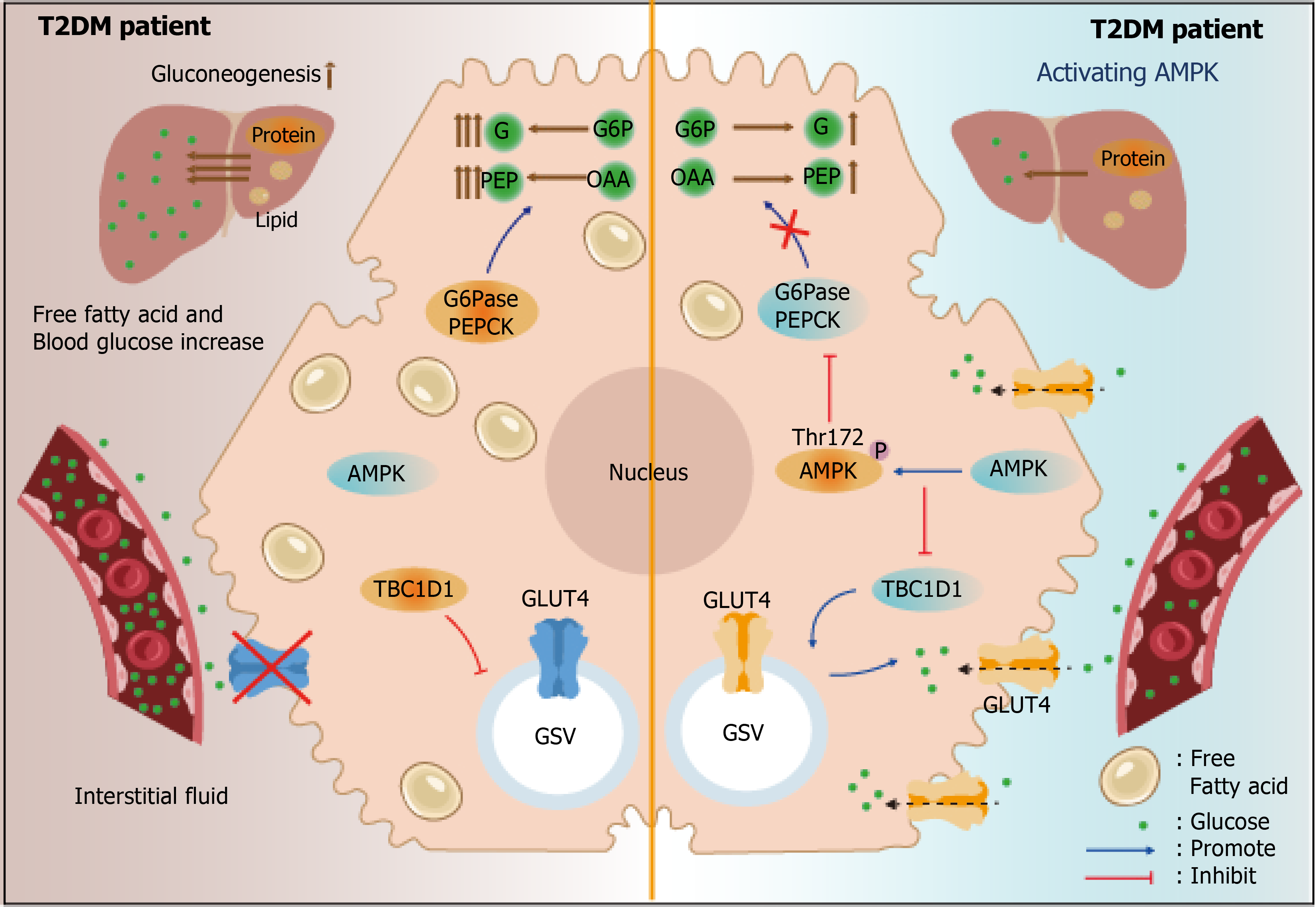
Figure 1 AMP-activated protein kinase activation in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, AMP-activated protein kinase promotes glucose transporter isoform 4 translocation from vesicles to the plasma membrane by inhibiting TBC1 domain family member 1, and inhibits liver gluconeogenesis by blocking the conversion of oxaloacetic acid to phosphoenolpyruvate and glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose, leading to reduced blood glucose. APMK: AMP-activated protein kinase; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; GLUT4: Glucose transporter isoform 4.
- Citation: Zhu JX, Pan ZN, Li D. Intracellular calcium channels: Potential targets for type 2 diabetes mellitus? World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 98995
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/98995.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.98995