Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 97201
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.97201
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.97201
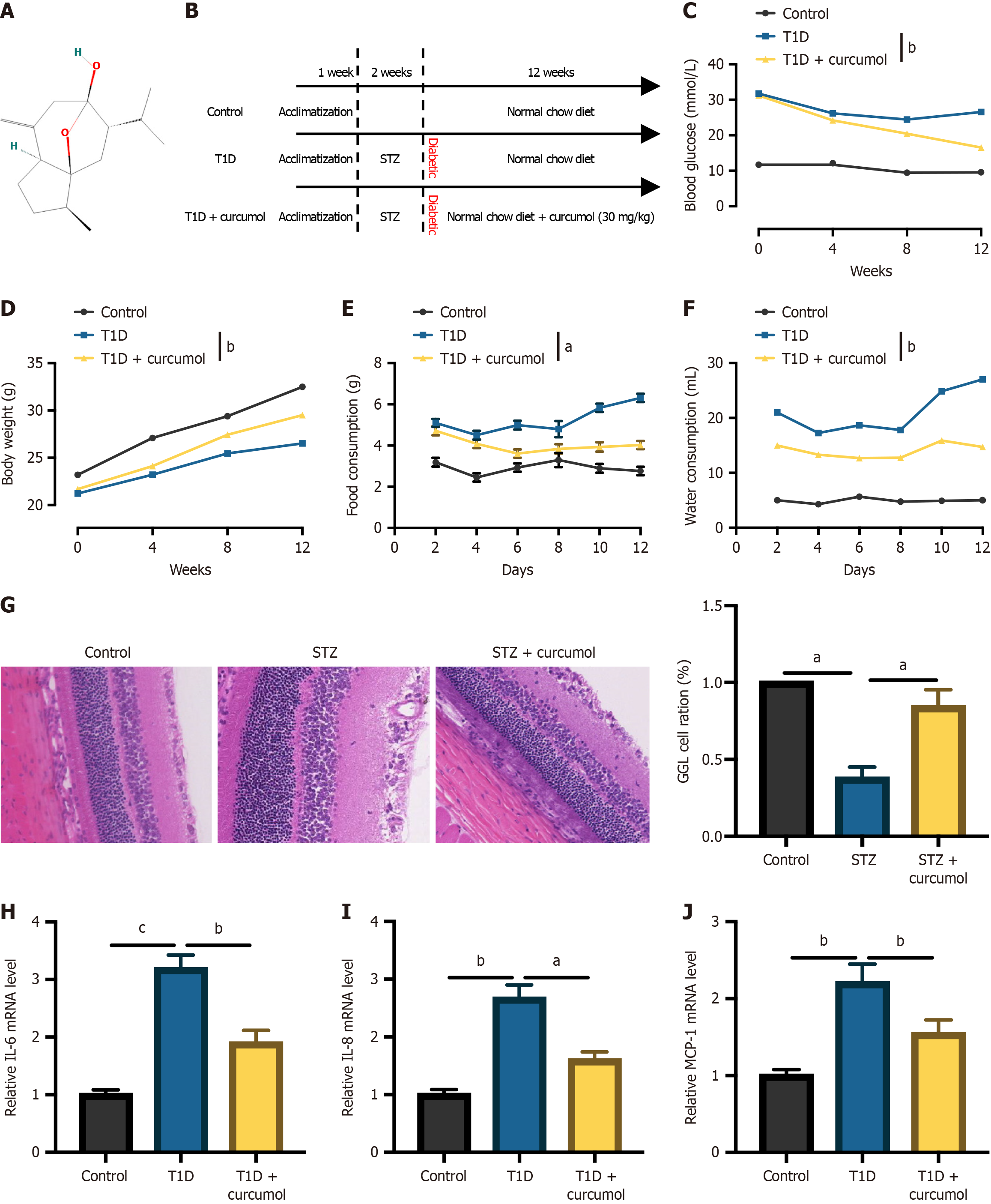
Figure 1 Curcumol attenuates diabetic retinopathy progression in mouse models.
A: The molecular configuration of curcumol; B: A schematic illustration of the animal model assembly; C: Systematic monitoring of blood glucose levels of all mice; D: Body weight measurements; E: Food intake; F: Water intake; G: Representative retinal morphology images obtained through hematoxylin and eosin staining; H-J: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of mRNA expression levels of pro-inflammatory factors, including interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Data represent the mean ± SD, n = 5-7 per group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. T1D: Type 1 diabetes; STZ: Streptozotocin; IL: Interleukin; MCP-1: Chemoattractant protein-1.
- Citation: Rong H, Hu Y, Wei W. Curcumol ameliorates diabetic retinopathy via modulating fat mass and obesity-associated protein-demethylated MAF transcription factor G antisense RNA 1. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 97201
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/97201.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.97201