Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 96176
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.96176
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.96176
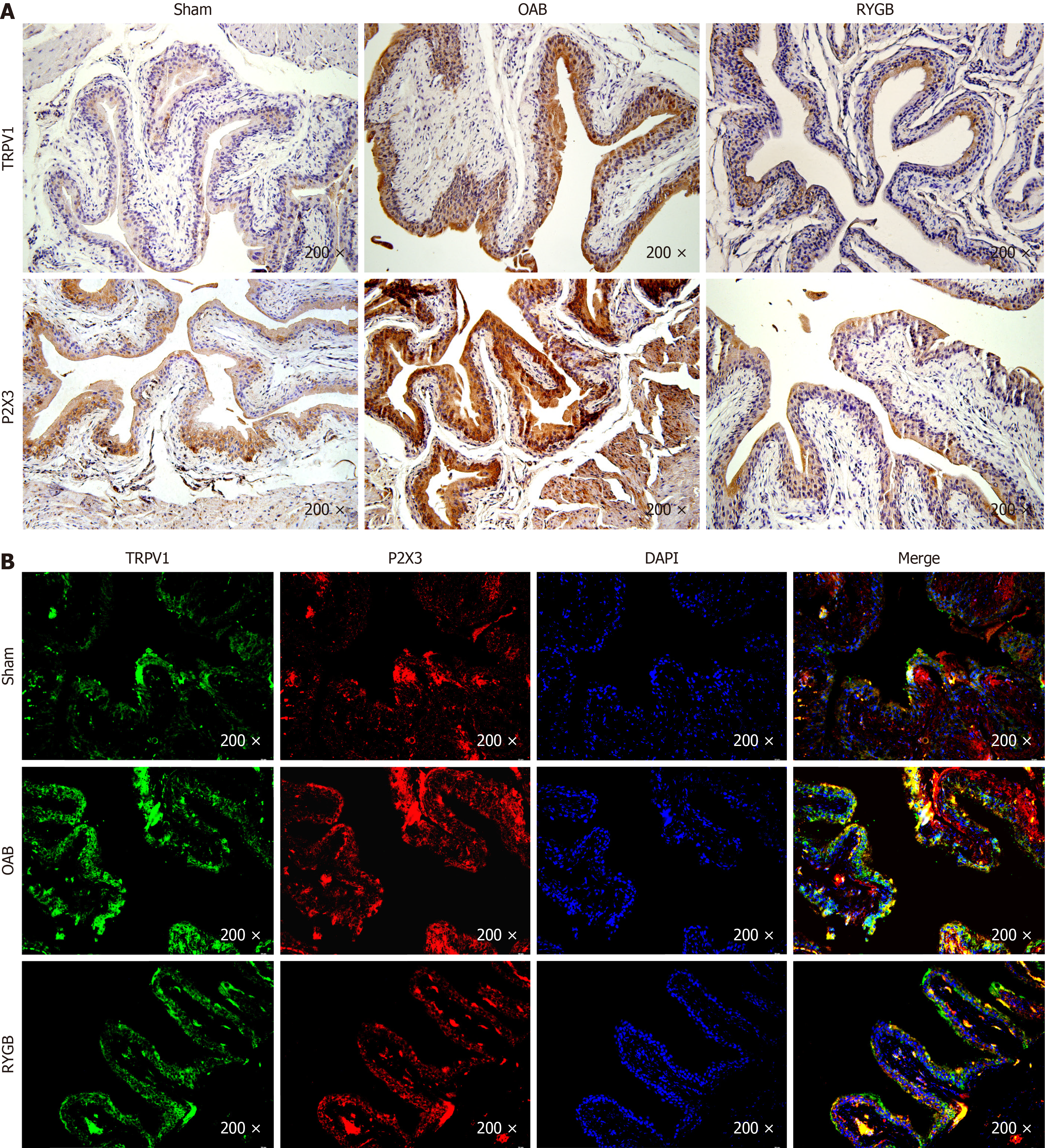
Figure 5 Expression and localization of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 and purinergic receptor P2X3 in bladder tissue.
A: Immunohistochemistry of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) and purinergic receptor P2X3 in bladder tissue (n = 8); B: Immunofluorescence colocalization of TRPV1 and P2X3 in bladder tissue (the green indicates TRPV1, the red indicates P2X3, and the yellow indicates coexpression of TRPV1 and P2X3; n = 8). RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; OAB: Overactive bladder.
- Citation: Li GY, Ren S, Huang BC, Feng JJ, Wang QQ, Peng QJ, Tian HF, Yu LY, Ma CL, Fan SZ, Chen XJ, Al-Qaisi MA, He R. Role and mechanism of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in the treatment of diabetic urinary bladder hyperactivity by reducing TRPV1 and P2X3. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 96176
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/96176.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.96176