Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 93630
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.93630
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.93630
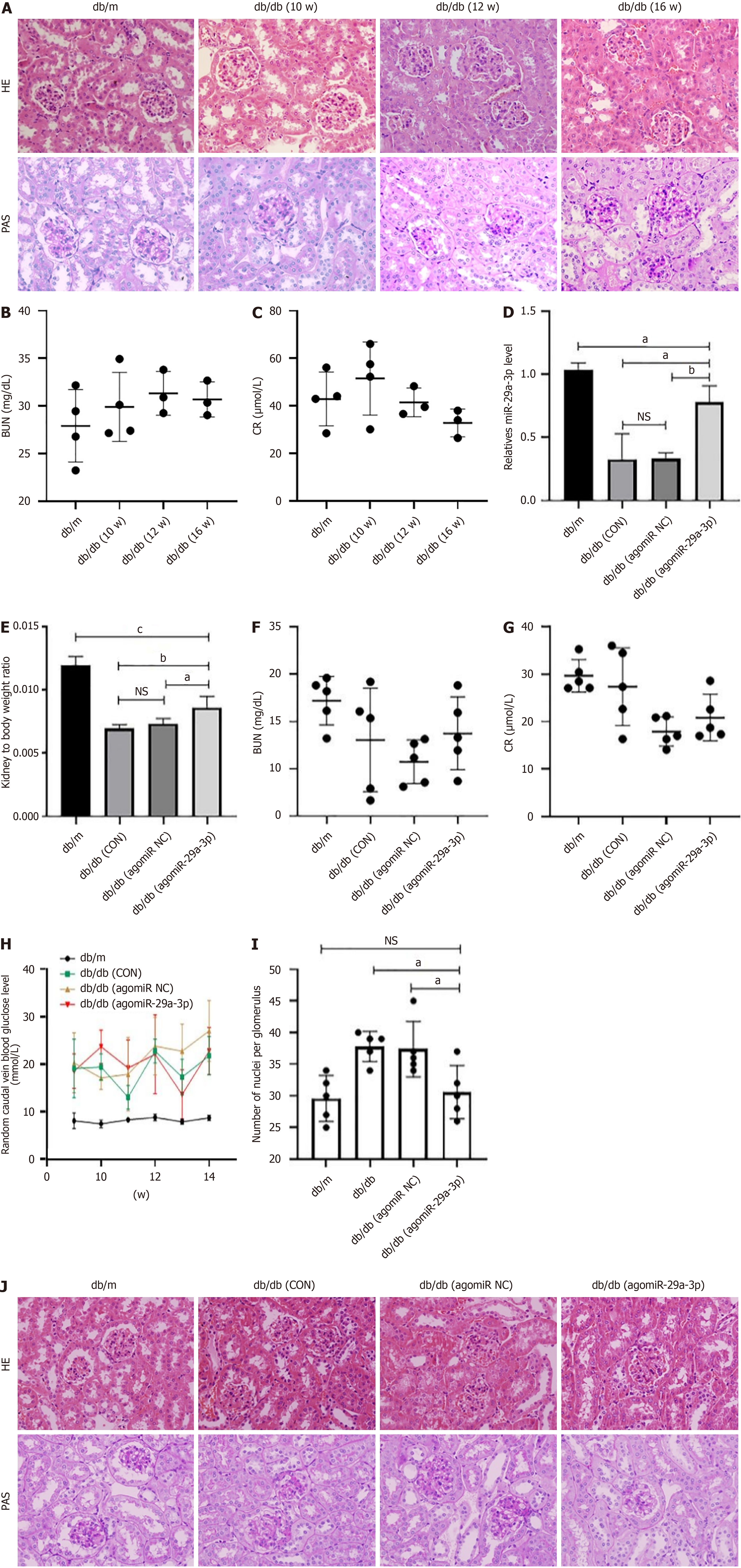
Figure 6 After antagomiR-29a-3p therapy, the renal index of diabetic mice increased, serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels were within the normal range, and the renal pathological changes were relieved.
A: Renal pathological changes in mice at 10, 12, and 16 weeks hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE), periodic acid-Schiff staining (PAS), × 400]; B and C: Results of serum creatinine (CR) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels in mice at different weeks of age; D: Quantitative reverse transcription PCR to detect the expression of miR-29a-3p; E: Renal index of diabetic (db/db) mice in each group (bilateral renal body weight/mouse body weight), (n = 5); F and G: Serum biochemical test results for mice in each group; H: Random caudal vein blood glucose levels; I and J: Renal pathological changes in the mice: The pathological changes in db/db (agomiR-29a-3p) mice were more severe than that in the db/m mice, but were less severe than that in the db/db mice without agomiR-29a-3p treatment. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. NS: Not significant; NC: Negative control; CON: Control group.
- Citation: Yang Y, Chen Y, Tang JY, Chen J, Li GQ, Feng B, Mu J. MiR-29a-3p inhibits fibrosis of diabetic kidney disease in diabetic mice via downregulation of DNA methyl transferase 3A and 3B. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 93630
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/93630.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.93630