Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 101916
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.101916
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.101916
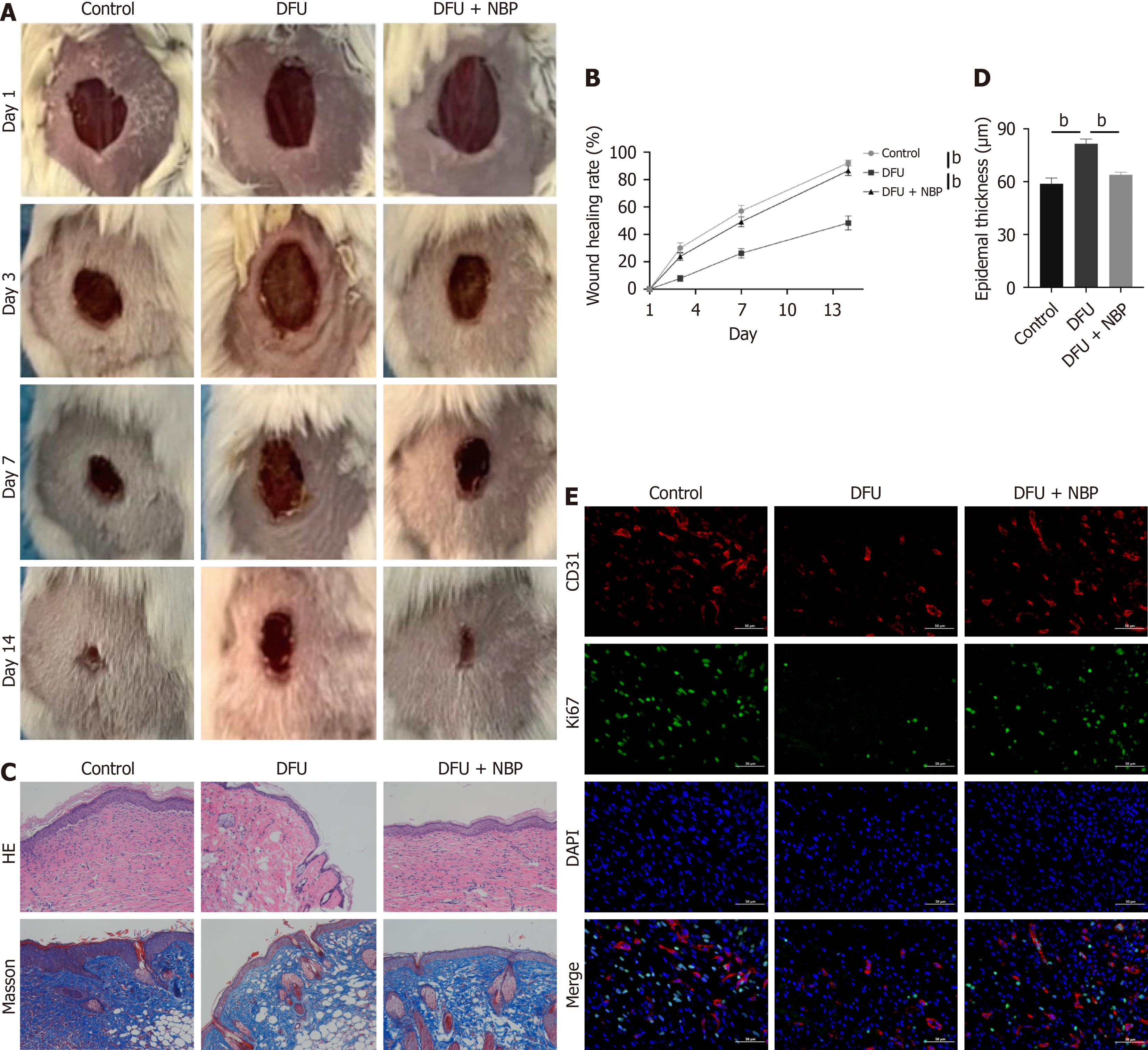
Figure 2 Wound healing of different time points in diabetic foot ulcers mice.
A: Images of mice wounds at different time points; B: The healing rate of foot wounds at different time points in mice; C: The wound tissues of mice were stained with hematoxylin-eosin and Masson 14 days after surgery; D: The epidermal thickness of mice 7 days after surgery; E: Immunofluorescence staining showed capillary density analysis of wound tissues in mice. Data expressed as individual values with mean ± SE. bP < 0.01. DFU: Diabetic foot ulcers; NBP: Dl-3-n-butylphthalide; HE: Hematoxylin-eosin.
- Citation: Wei WH, Bai YL, Zhu D, Zhang JY, Yin QC, Li Q, Shen CQ, Jin PS. Dl-3-n-butylphthalide ameliorates diabetic foot ulcer by inhibiting apoptosis and promoting angiogenesis. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 101916
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/101916.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.101916