Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 101384
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.101384
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.101384
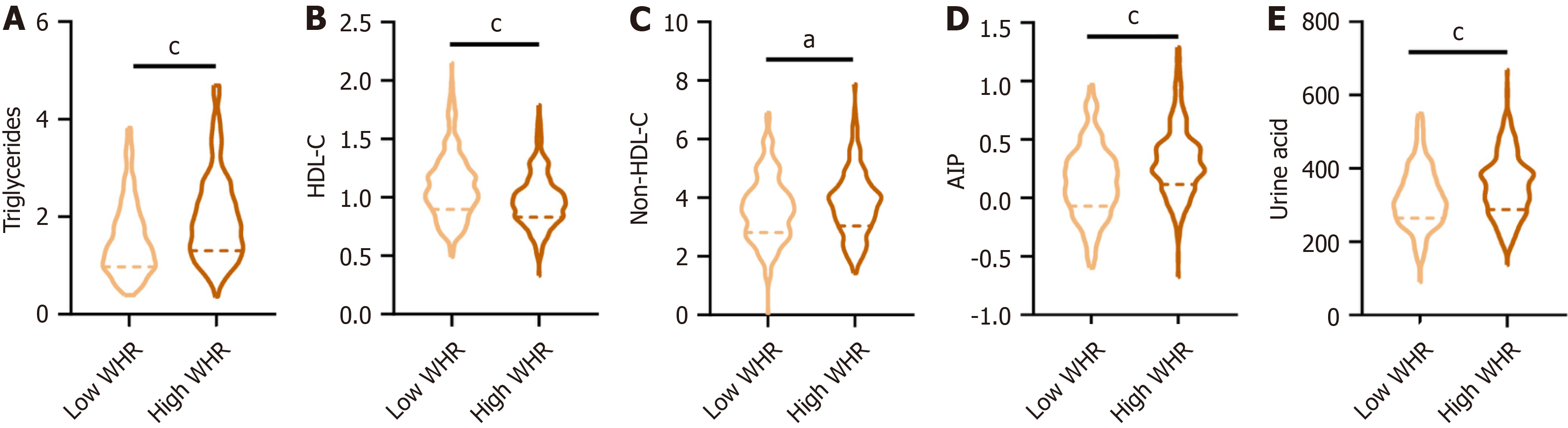
Figure 3 Impact of different waist-to-hip ratio level on serum lipids and renal function in type 2 diabetic mellitus patients.
A: Levels of triglyceride (TG); B: Levels of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C); C: Levels of the data of log (TG/HDL-C); D: Levels of urine acid; E: Levels of HDL-C. Low waist-to-hip ratio: 0.7556-0.9451; High waist-to-hip ratio: 0.9452-1.1319; WHR: Waist-to-hip ratio; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; AIP: The data of log (triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol).
- Citation: Lin DN, Li D, Peng MM, Yang H, Lin ZZ, Ye EL, Chen WT, Zhou MX, Huang XE, Lu XM. Elevated waist-to-hip ratio, as an abdominal obesity index, predicts the risk of diabetic kidney injury. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 101384
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/101384.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.101384