Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2025; 16(4): 100113
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.100113
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.100113
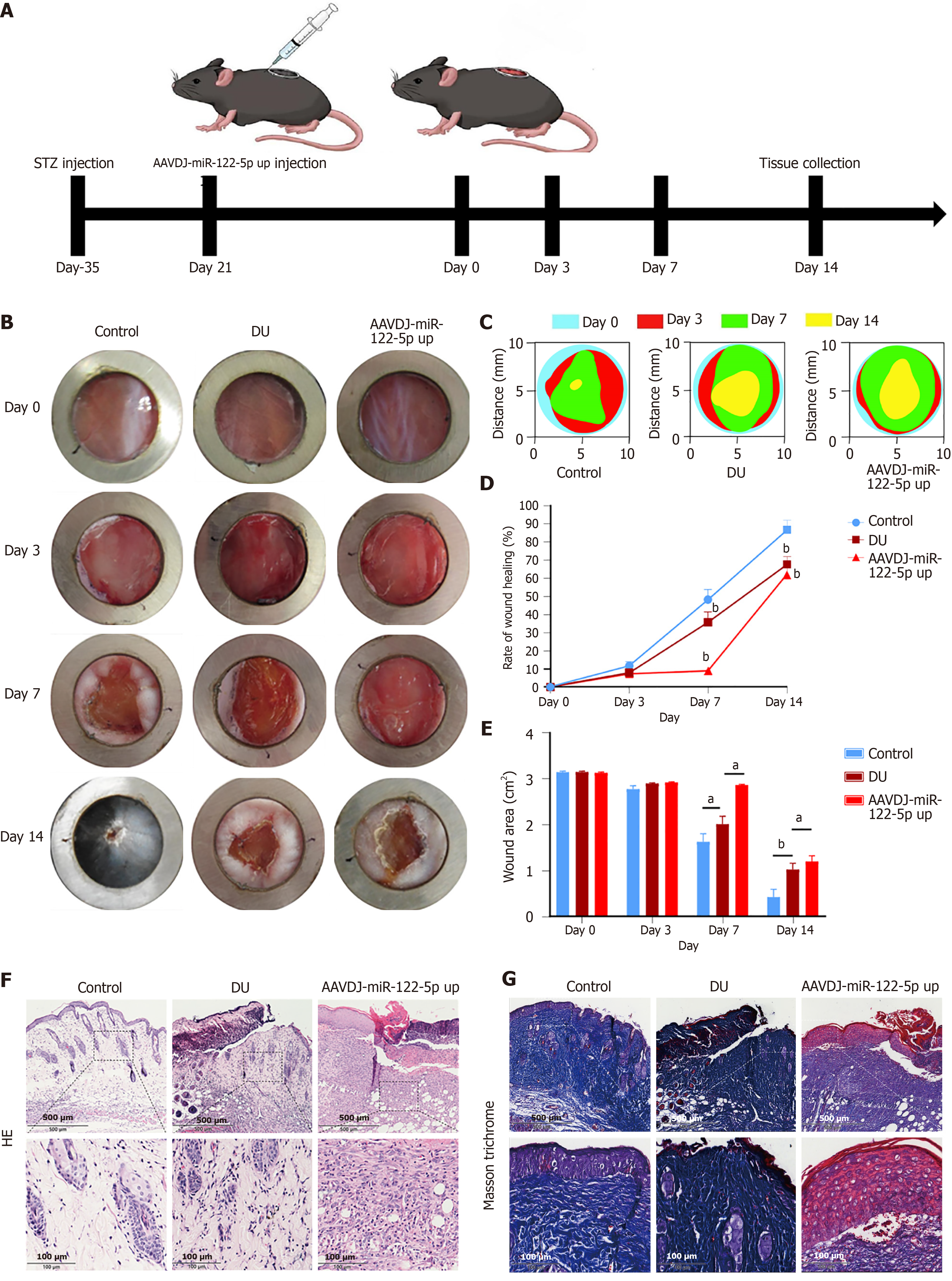
Figure 2 Adeno-associated virus-DJ-microRNA-122-5p up-decelerated wound healing in diabetic mice.
A: Schematic diagram of the timeline of mice tests on the therapeutic effect of wound; B-D: A full-thickness skin wound was created on the dorsal area of the mice (1 cm × 1 cm). Animals were randomized into three groups and treated with phosphate-buffered saline. Optical pictures and related quantification of the wound closure rate in the control, diabetic ulcer (DU), and adeno-associated virus (AAV)-DJ-microRNA (miR)-122-5p groups at days 0, 3, 7, and 14 after the skin operation (n = 5); E: Gross view of wounds and wound area among the three groups of mice; F: Hematoxylin-eosin staining images of wound tissues in the control, DU, and AAVDJ-miR-122-5p groups at day 14 (n = 5; scale bar = 500 μm for 10 × and 100 μm for 40 ×); G: Masson trichrome staining at day 14 post operation (n = 5, scale bar = 500 μm for 10 × and 100 μm for 40 ×). aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. DU: Diabetic ulcer; miR: MicroRNA; AAVDJ: Adeno-associated virus-DJ; STZ: Streptozotocin; HE: Hematoxylin-eosin.
- Citation: Yuan MJ, Huang HC, Shi HS, Hu XM, Zhao Z, Chen YQ, Fan WJ, Sun J, Liu GB. MicroRNA-122-5p is upregulated in diabetic foot ulcers and decelerates the transition from the inflammatory to the proliferative stage. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(4): 100113
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i4/100113.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.100113