Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2025; 16(3): 99277
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.99277
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.99277
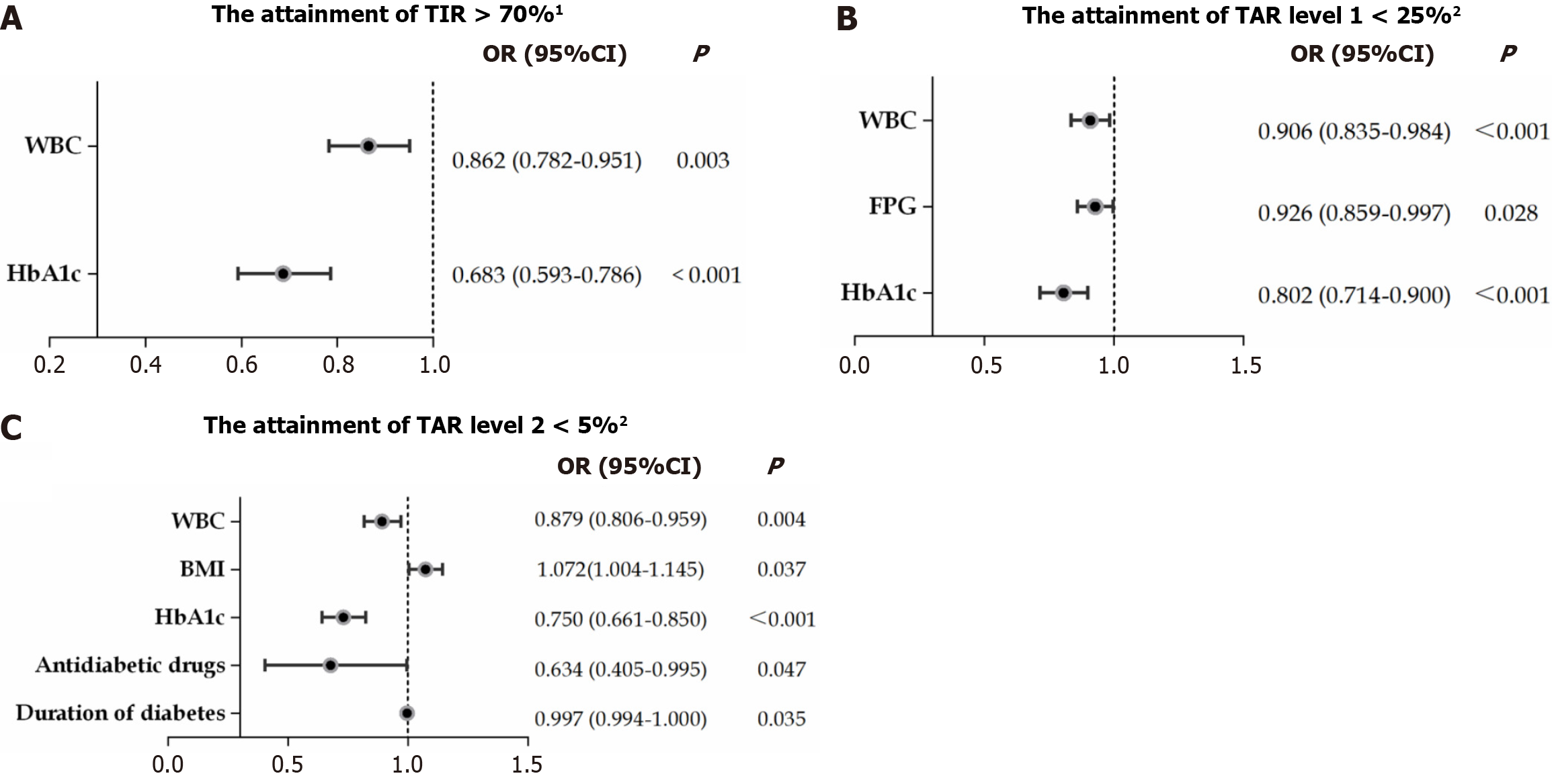
Figure 4 Logistic regression analysis of the proportion of continuous glucose monitoring metrics meeting the standards and their influencing factors.
A: The attainment of time in range > 70%; B: The attainment of time above range (TAR) level 1 < 25%; C: The attainment of TAR level 2 < 5%. 1Adjusted for sex, age, body mass index (BMI), duration of diabetes, duration of diabetic foot, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, white blood cell (WBC), fasting plasma glucose (FPG), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), Wagner grade, antidiabetic drugs. 2Adjusted for sex, age, BMI, duration of diabetes, duration of diabetic foot, WBC, FPG, HbA1c, antidiabetic drugs. TAR: Time above range; TIR: Time in range. WBC: White blood cell; HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; BMI: Body mass index; FPG: Fasting plasma glucose.
- Citation: Geng XQ, Chen SF, Wang FY, Yang HJ, Zhao YL, Xu ZR, Yang Y. Correlation between key indicators of continuous glucose monitoring and the risk of diabetic foot. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(3): 99277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i3/99277.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.99277