Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2025; 16(3): 98590
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.98590
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.98590
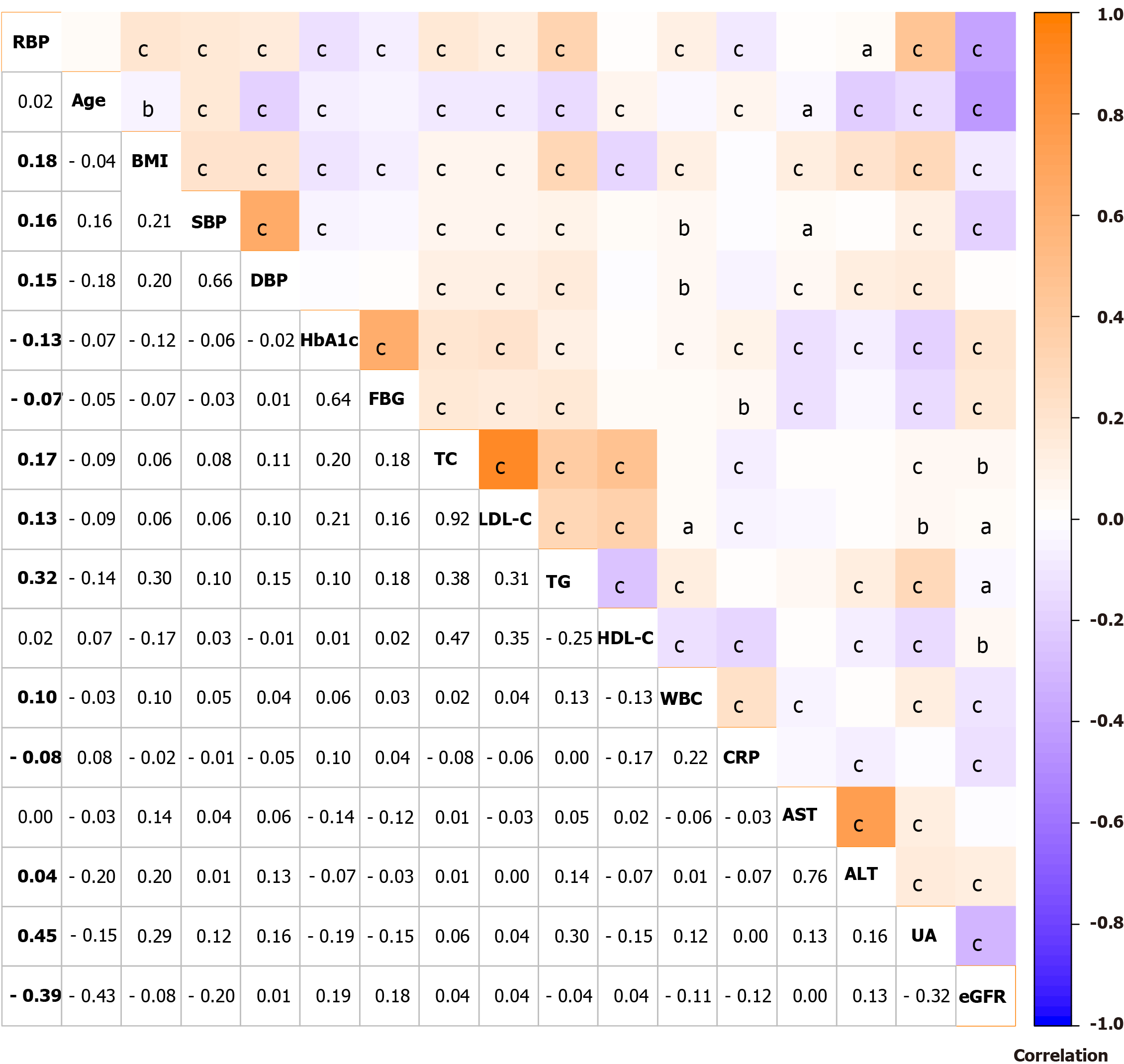
Figure 2 Correlation between serum retinol-binding protein level and type 2 diabetes mellitus patient clinical indicators.
Orange indicates a positive correlation, whereas blue indicates a negative correlation. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. RBP: Retinol-binding protein; BMI: Body mass index; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; HbA1c: Glycated hemoglobin; FBG: Fasting blood glucose; TC: Total cholesterol; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: Triglycerides; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; WBC: White blood cell; CRP: C-reactive protein; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; UA: Uric acid; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate.
- Citation: Zhang YL, Peng GL, Leng WL, Lian Y, Cheng LQ, Li X, Wang YL, Zhou L, Long M. Association between serum retinol-binding protein and lower limb atherosclerosis risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(3): 98590
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i3/98590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.98590