Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2025; 16(3): 97544
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.97544
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.97544
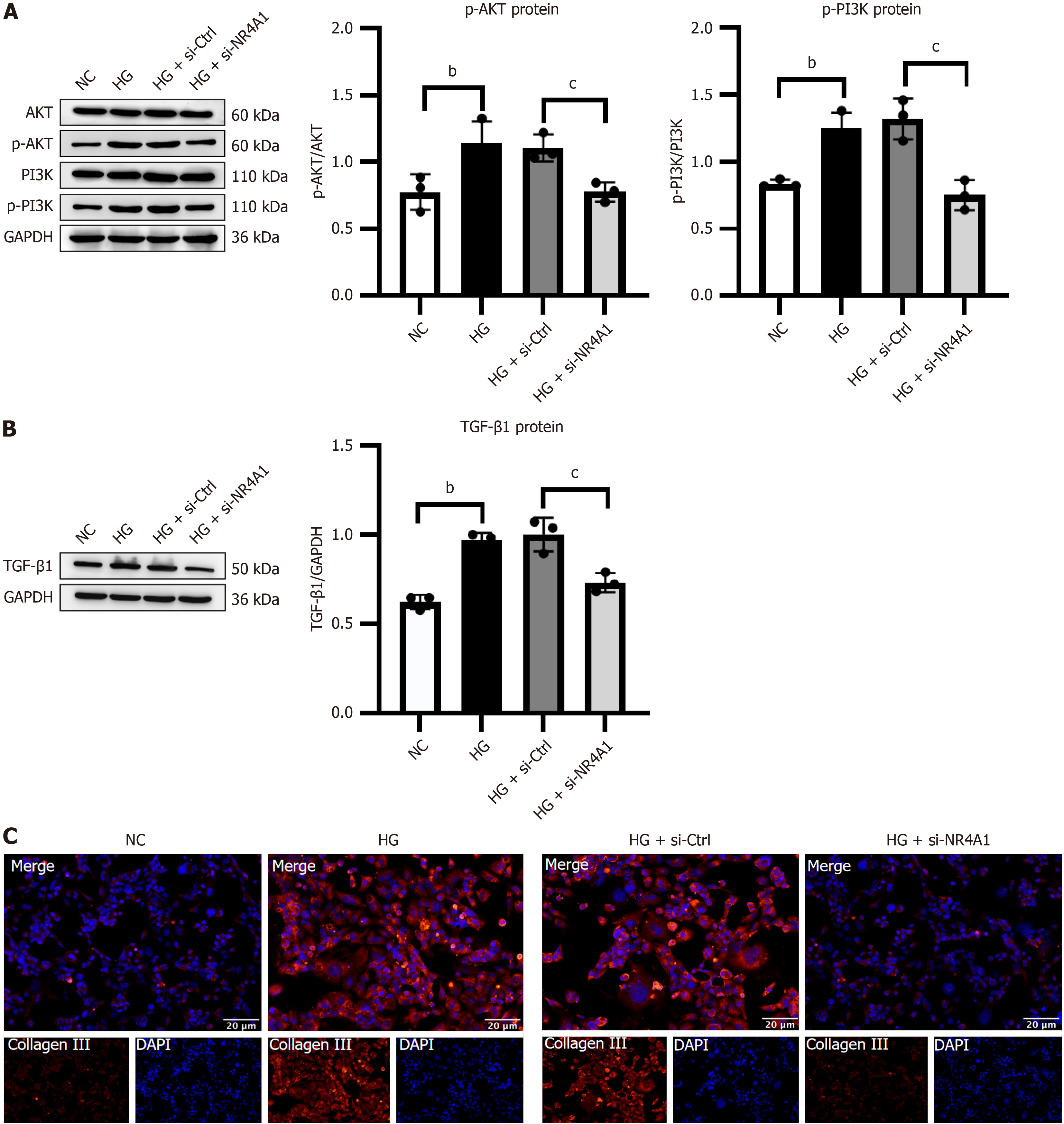
Figure 6 Silencing of nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 attenuated phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway-mediated fibrosis in high glucose-activated HK-2 cells.
A: Illustrative Western blotting bands and integrated density analysis of protein kinase B (AKT), p-AKT, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and p-PI3K in HK-2 cells; B: Representative western blotting and integrated density analysis of transforming growth factor-β1 in HK-2 cells; C: Illustrative immunocytochemistry images of collagen III in HK-2 cells. Scale bar = 20 μm, n = 3. bP < 0.05 vs normal control, cP < 0.05 vs high glucose + negative control. HG: High glucose; NC: Normal control; NR4A1: Nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1; AKT: Protein kinase B; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; si-NR4A1: SiRNA targeting nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1.
- Citation: Li JM, Song ZH, Li Y, Chen HW, Li H, Yuan L, Li J, Lv WY, Liu L, Wang N. NR4A1 silencing alleviates high-glucose-stimulated HK-2 cells pyroptosis and fibrosis via hindering NLRP3 activation and PI3K/AKT pathway. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(3): 97544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i3/97544.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.97544