Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2025; 16(3): 95092
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.95092
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.95092
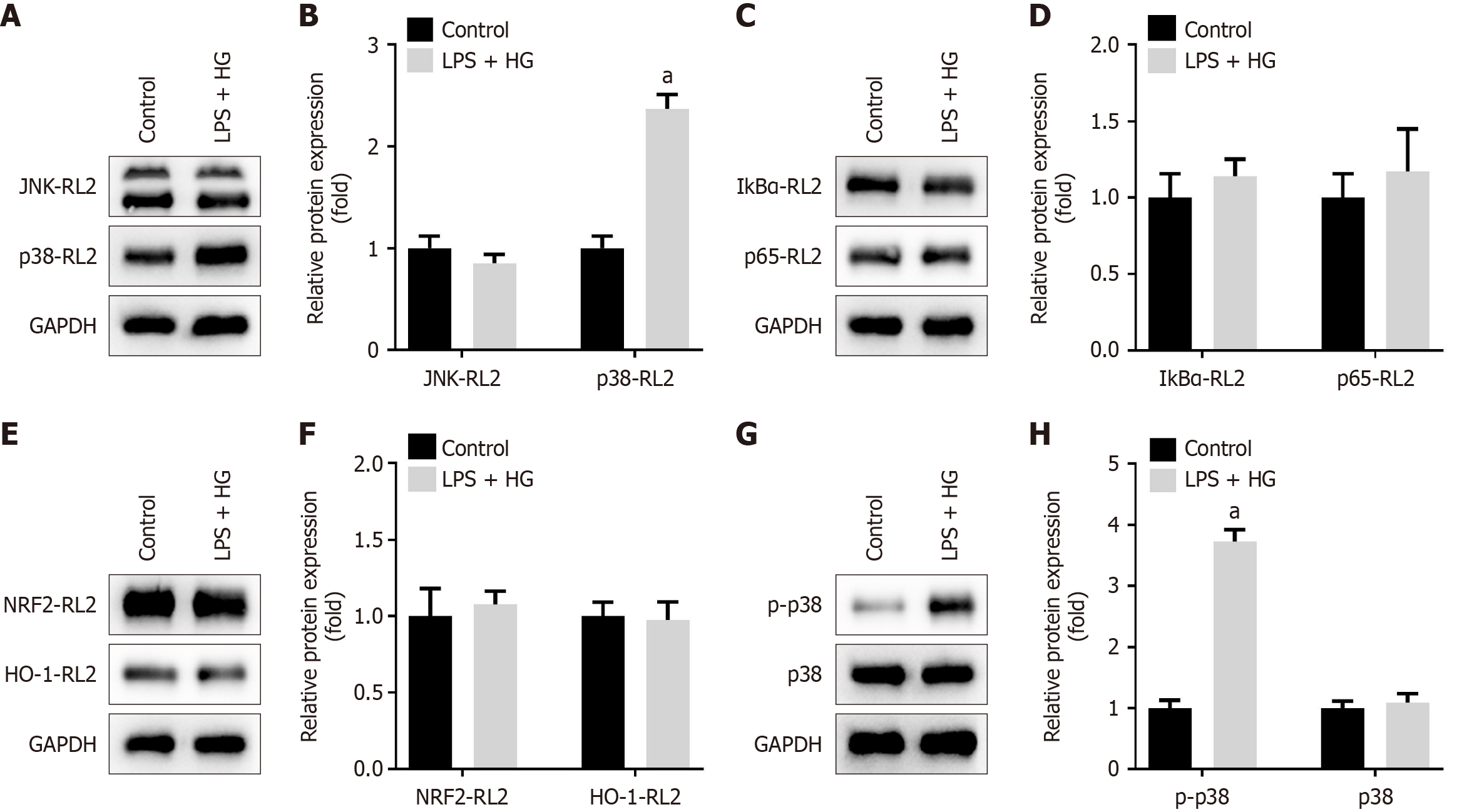
Figure 9 Lipopolysaccharide and high glucose activate the p38/major mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
A and B: O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAcylation) levels of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 were measured and quantified using Western blot after immunoprecipitation (IP) of these proteins; C and D: O-GlcNAcylation levels of inhibitor of κB alpha and p65 were measured and quantified using Western blot after IP; E and F: O-GlcNAcylation levels of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 and heme oxygenase 1 were measured and quantified using Western blot after IP; G and H: Protein levels of p38 and phosphorylated p38 were examined and quantified using Western blot. aP < 0.05. P value calculated vs control. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; HG: High glucose; NRF2: Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; RL2: O-GlcNAc; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; IκBα: Inhibitor of κB alpha; HO-1: Heme oxygenase 1; p-p38: Phosphorylated p38; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Wu YK, Liu M, Zhou HL, He X, Wei J, Hua WH, Li HJ, Yuan QH, Xie YF. O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase regulates macrophage polarization in diabetic periodontitis: In vivo and in vitro study. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(3): 95092
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i3/95092.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.95092