Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2025; 16(3): 102277
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.102277
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.102277
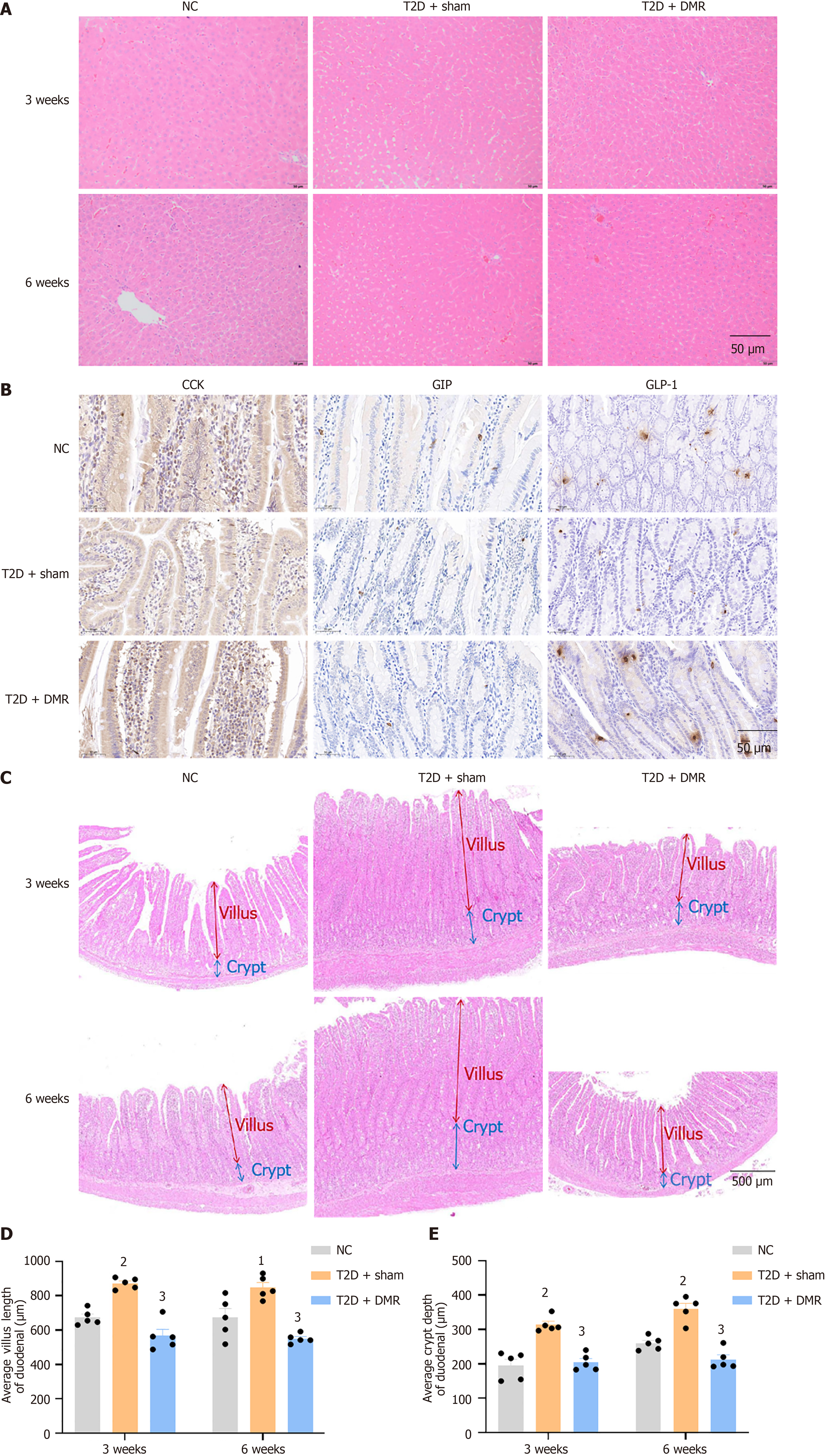
Figure 3 Effects of duodenal mucosal resurfacing procedure on liver, enteroendocrine cells, duodenal villi, and crypts in type 2 diabetes rats.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of the liver in normal control (NC), type 2 diabetes (T2D) + sham and T2D + duodenal mucosal resurfacing (DMR) rats at postoperative weeks 3 and 6 (n = 5 mice per group, Scale bar = 50 μm); B: Immunohistochemical analyses of duodenal cholecystokinin, gastric inhibitory peptide, glucagon-like peptide 1 in NC, T2D + sham and T2D + DMR rats at postoperative weeks 6 (n = 4 mice per group, Scale bar = 50 μm); C: HE staining of the duodenum in NC, T2D + sham and T2D + DMR rats at postoperative weeks 3 and 6 (n = 5 mice per group, Scale bar = 500 μm); D and E: The villus length and crypt depth in NC, T2D + sham and T2D + DMR rats at postoperative weeks 3 and 6 (n = 5 mice per group). Data are presented as mean ± SE. 1P < 0.01 vs normal control group. 2P < 0.001 vs normal control group. 3P < 0.001 vs type 2 diabetes-sham group. DMR: Duodenal mucosal resurfacing; T2D: Type 2 diabetes; NC: Normal control; CCK: Cholecystokinin; GIP: Gastric inhibitory peptide; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide 1.
- Citation: Nie LJ, Cheng Z, He YX, Yan QH, Sun YH, Yang XY, Tian J, Zhu PF, Yu JY, Zhou HP, Zhou XQ. Role of duodenal mucosal resurfacing in controlling diabetes in rats. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(3): 102277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i3/102277.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.102277