Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2024; 15(9): 1962-1978
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962
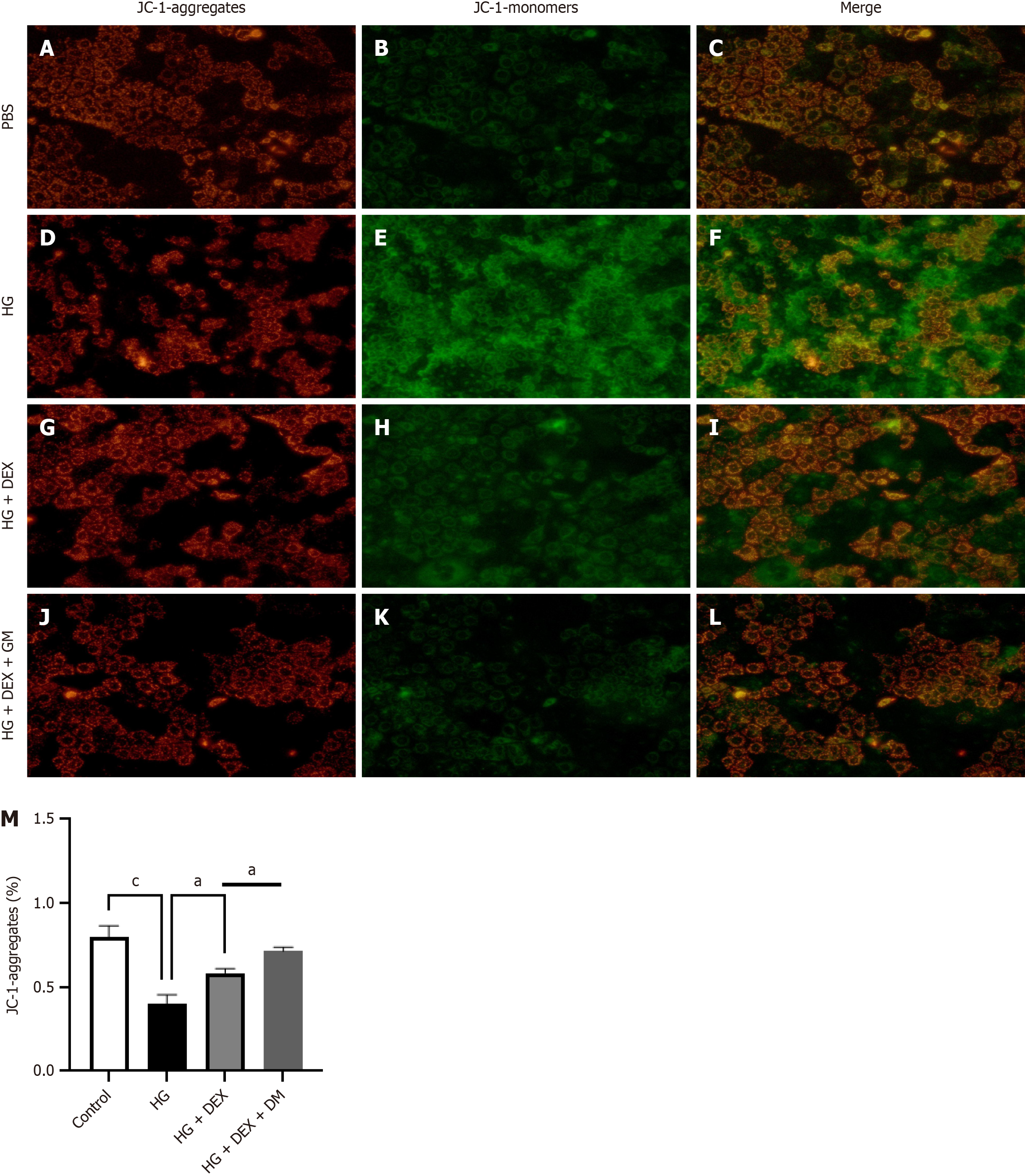
Figure 10 Dexmedetomidine induces mitochondrial impairment in Caco-2 cells in vitro.
A-M: During inflammation, mitochondrial oxidative energy metabolism plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of the gut epithelial barrier. We investigated the potential effects of dexmedetomidine on high glucose-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in Caco-2 cells. Comparative analysis revealed that dexmedetomidine treatment, as opposed to high glucose treatment alone, substantially reduced mitochondrial dysfunction, manifested through reduced levels of JC-1 monomers and enhanced ΔΨm. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001. HG: High glucose; DEX: Dexmedetomidine; PBS: Phosphate buffer saline; GM: GM6001.
- Citation: Lu M, Guo XW, Zhang FF, Wu DH, Xie D, Luo FQ. Dexmedetomidine ameliorates diabetic intestinal injury by promoting the polarization of M2 macrophages through the MMP23B pathway. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(9): 1962-1978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i9/1962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962