Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2024; 15(9): 1962-1978
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962
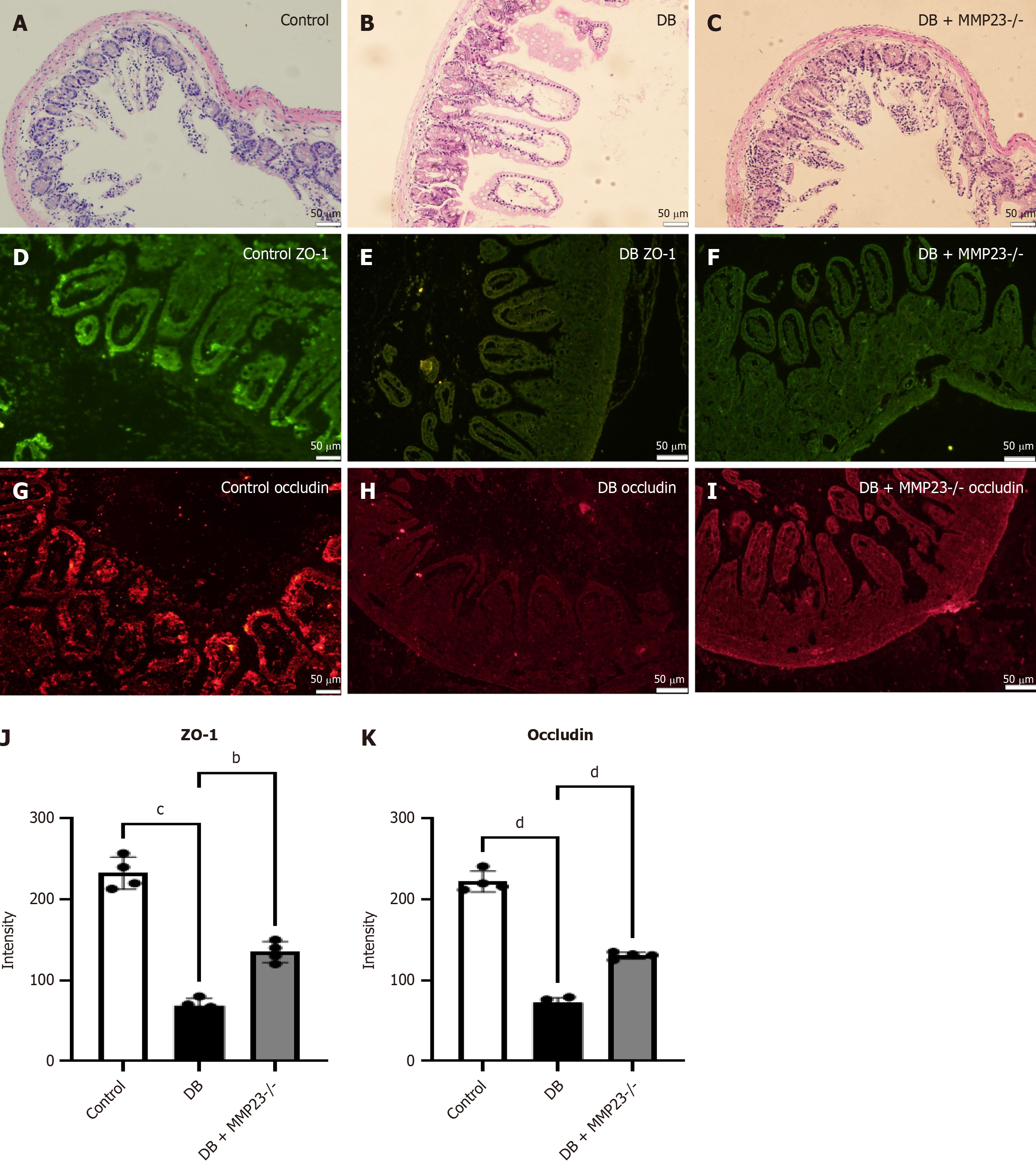
Figure 5 The severity of diabetes-induced intestinal injury was positively correlated with MMP23 expression in mice.
MMP23 KO mice were used to investigate the role of MMP23 in intestinal injury. A-C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed a less severe injury in the intestines of MMP23 knockout mice; D-I: Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated a significant reduction in the intestinal injury marker after 24 hours of treatment; J and K: The protein expression of occludin and ZO-1 was significantly upregulated following MMP23 knockout, as revealed by immunofluorescence analysis. Scale bar = 50 μm. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. DB: Diabetes group.
- Citation: Lu M, Guo XW, Zhang FF, Wu DH, Xie D, Luo FQ. Dexmedetomidine ameliorates diabetic intestinal injury by promoting the polarization of M2 macrophages through the MMP23B pathway. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(9): 1962-1978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i9/1962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962