Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2024; 15(9): 1962-1978
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962
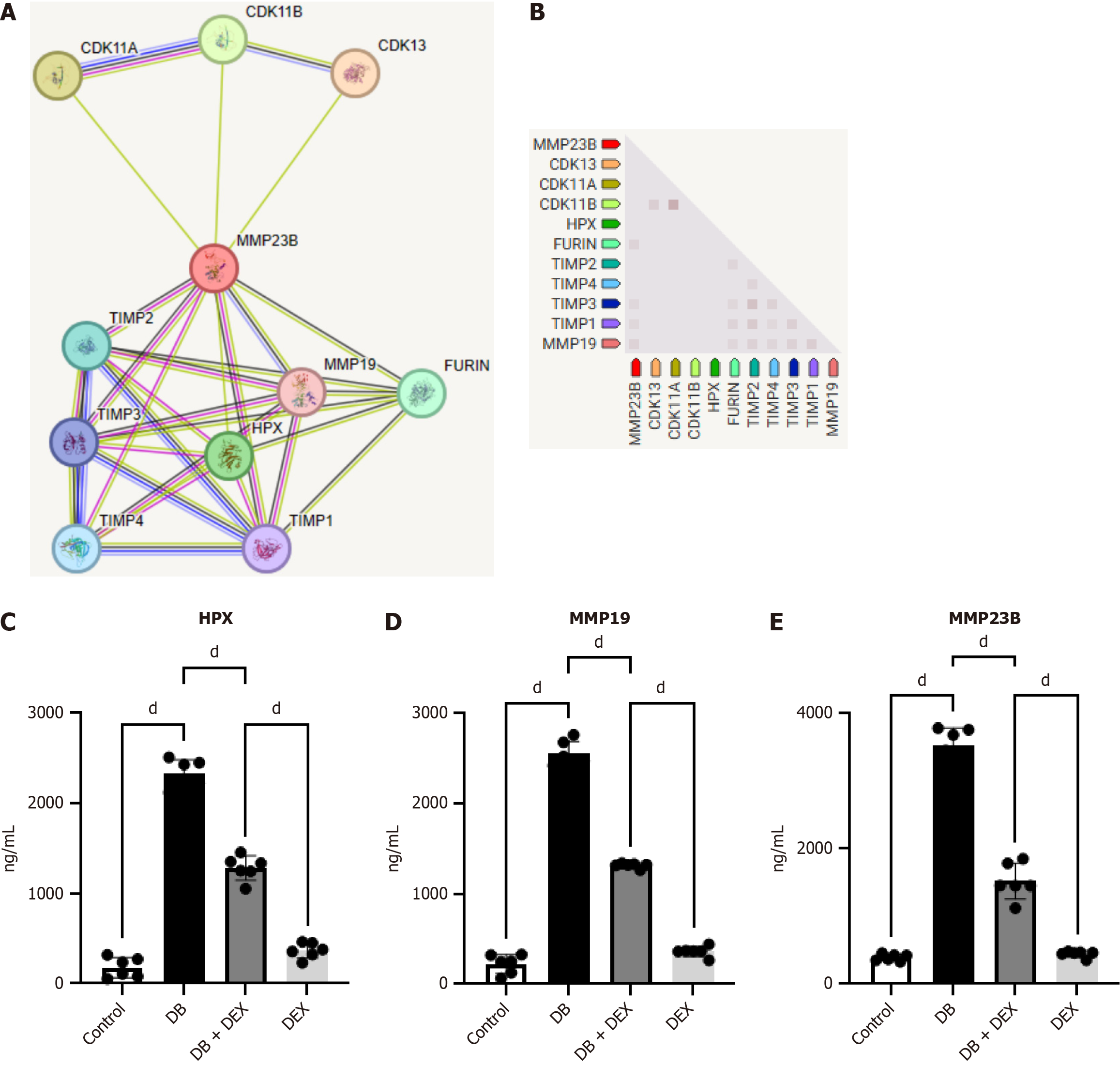
Figure 4 Protein-protein interaction network analysis and detected inflammatory factors.
The protein-protein interaction network comprised five nodes representing molecular pathways and processes associated with the five core differentially expressed genes. A and B: Working modules were developed using the MCODE plugin for Cytoscape; C-E: The results revealed a module of nine genes. The expressions of HPX, MMP19, and MMP23 were elevated in the diabetes group. The expression levels of inflammatory factors decreased upon dexmedetomidine compared with those in the control group. dP < 0.0001. DB: Diabetes group; DEX: Dexmedetomidine.
- Citation: Lu M, Guo XW, Zhang FF, Wu DH, Xie D, Luo FQ. Dexmedetomidine ameliorates diabetic intestinal injury by promoting the polarization of M2 macrophages through the MMP23B pathway. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(9): 1962-1978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i9/1962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962