Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2024; 15(9): 1942-1961
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1942
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1942
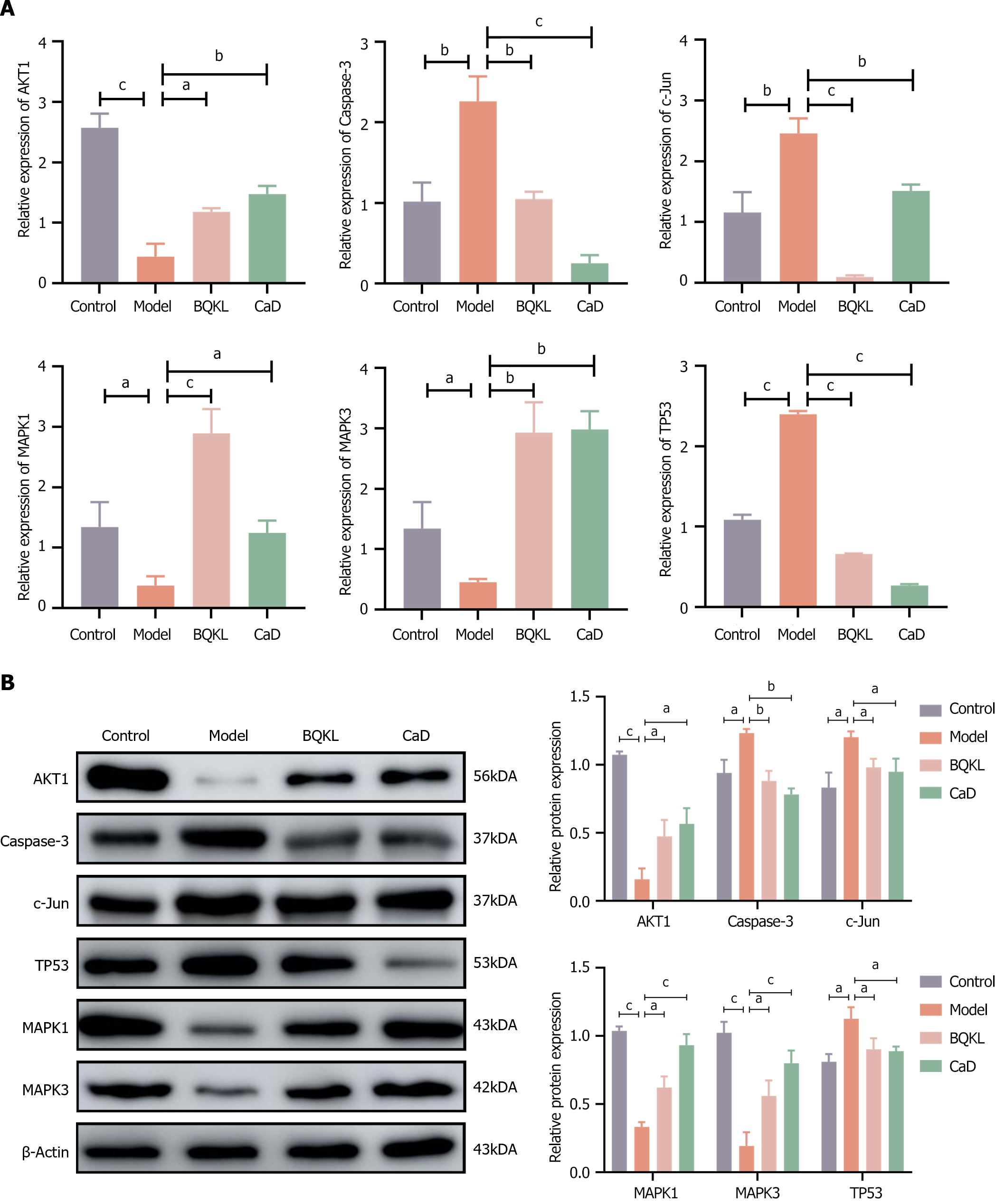
Figure 9 A molecular biological perspective on the role of Buqing granule in the diabetic retinopathy treatment.
A: Caspase-3, AKT1, c-Jun, TP53, MAPK1, and MAPK3 mRNA expression levels determined by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR; B: Protein expression levels determined by western blotting. The sequence from left to right represents the control group, the model group, the Buqing granule group and the calcium dobesilate group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. BQKL: Buqing granule; CaD: Calcium dobesilate.
- Citation: Yang YF, Yuan L, Li XY, Liu Q, Jiang WJ, Jiao TQ, Li JQ, Ye MY, Niu Y, Nan Y. Molecular mechanisms of Buqing granule for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy: Network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(9): 1942-1961
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i9/1942.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1942