Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2024; 15(9): 1916-1931
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1916
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1916
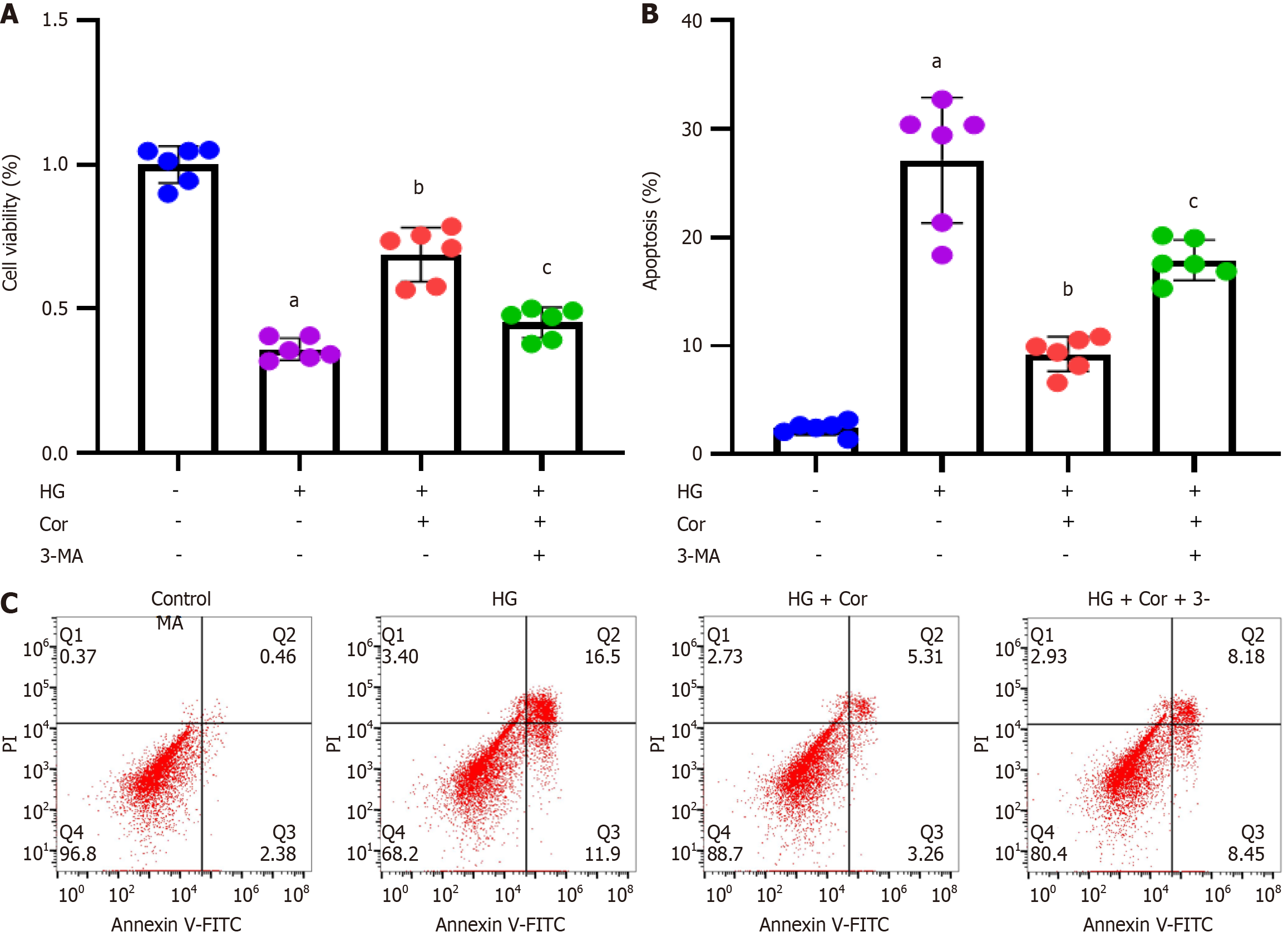
Figure 9 Corilagin attenuates podocyte damage induced by hyperglycemia by enhancing autophagy.
MPC5 cells were treated with the autophagy inhibitor 3-MA (1 mg/mL), corilagin (50 μM), and high glucose (D-glucose 30 mM) for 48 h. A: The effect of corilagin on cell viability was assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay; B: Cell apoptosis was assessed by Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide double staining using flow cytometry; C: Representative images of flow cytometry. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.001 vs control group; bP < 0.001 vs HG group; cP < 0.001 vs HG + Cor group. HG: High glucose; Cor: Corilagin.
- Citation: Lou Y, Luan YT, Rong WQ, Gai Y. Corilagin alleviates podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy by regulating autophagy via the SIRT1-AMPK pathway. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(9): 1916-1931
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i9/1916.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1916