Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2024; 15(9): 1916-1931
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1916
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1916
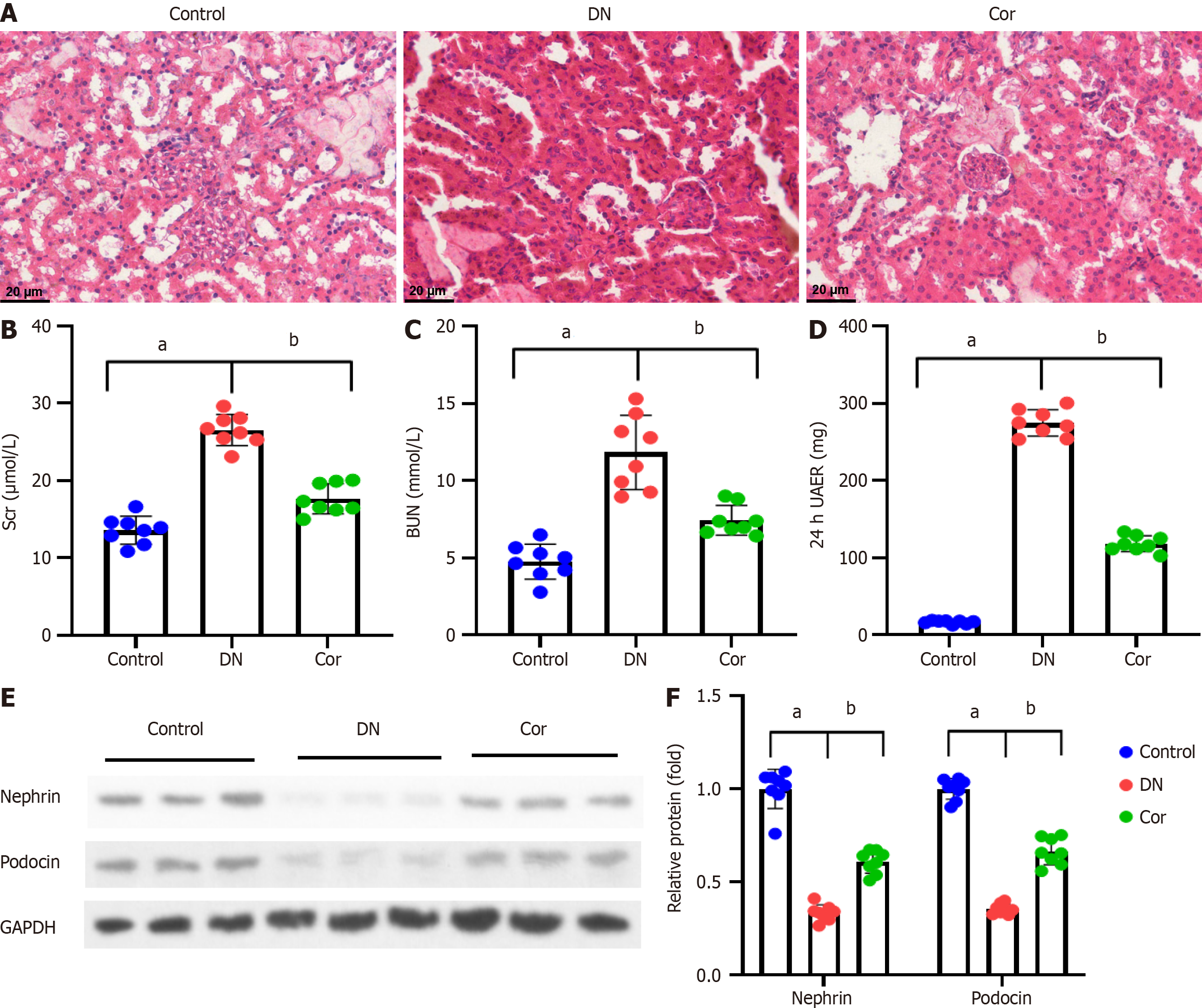
Figure 2 Corilagin improves histopathological injury and renal function of diabetic nephropathy mice.
A: Pathological changes of renal tissues assessed by hematoxylin and eosin staining in mice (magnification 400 ×); B and C: Serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen in mice detected using an automated biochemical analyzer; D: ELISA detection of urine microalbuminuria to calculate 24-h urinary albumin excretion rate; E: Western blot showing representative bands of Nephrin and Podocin in mouse kidney tissues; F: Quantification analysis of Nephrin and Podocin protein bands. Protein expression was normalized to GADPH. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 8 in each group). aP < 0.001 vs control group; bP < 0.001 vs DN group. Scr: Serum creatinine; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; 24-h UAER: 24-h urinary albumin excretion rate; Cor: Corilagin; DN: Diabetic nephropathy.
- Citation: Lou Y, Luan YT, Rong WQ, Gai Y. Corilagin alleviates podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy by regulating autophagy via the SIRT1-AMPK pathway. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(9): 1916-1931
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i9/1916.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1916