Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2024; 15(8): 1764-1777
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i8.1764
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i8.1764
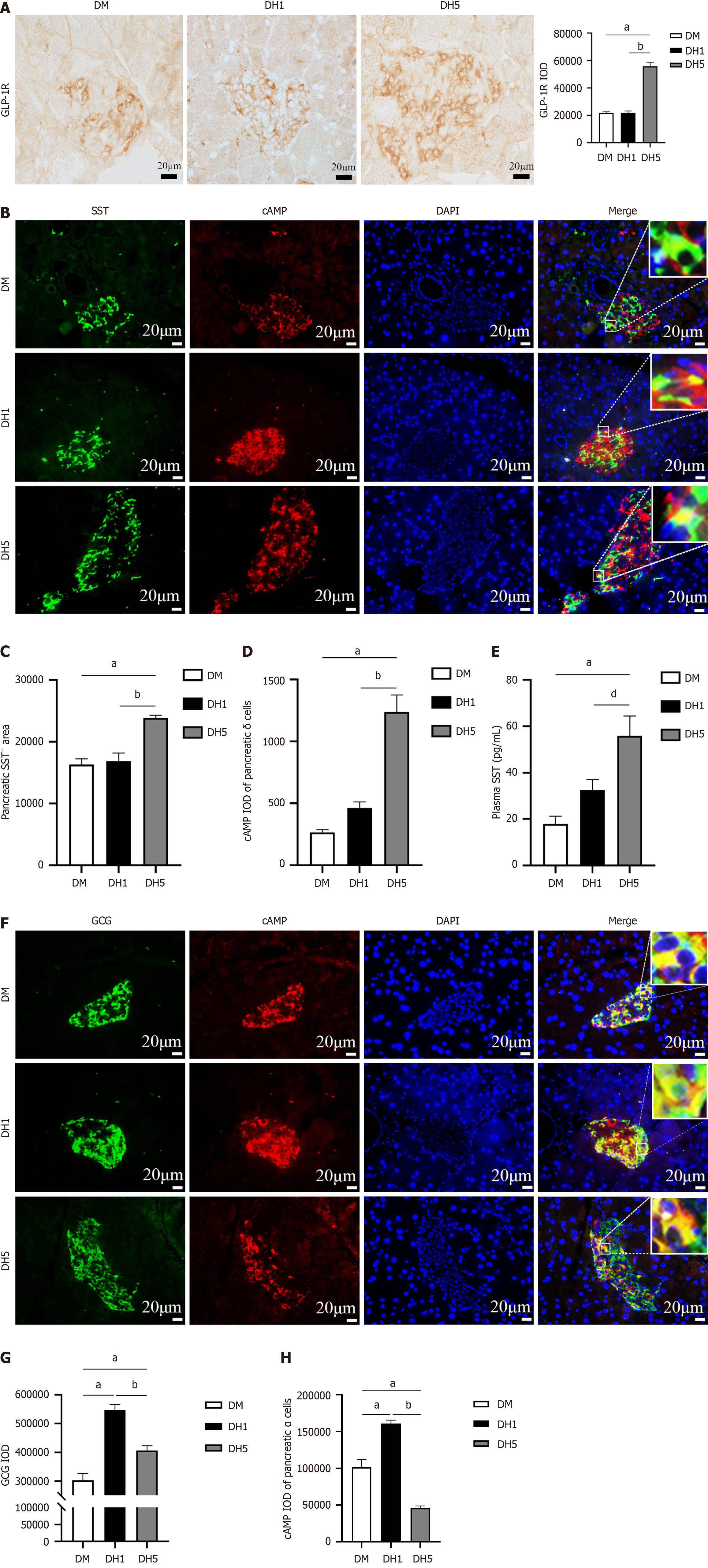
Figure 4 Intestinal glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits glucagon secretion through endocrine effects.
A: Immunohistochemistry showing pancreatic glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) levels, with GLP-1R in brown. Bars = 20 μm; B: Immunofluorescence staining showing somatostatin (SST) + cAMP expression in the pancreas, with SST in green, cAMP in red, and cell nuclei in blue. Bars = 20 μm; C: Pancreatic SST+ cell area; D: CAMP integrated optical density (IOD) in pancreatic δ cells; E: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results showing changes in plasma SST levels; F: Immunofluorescence staining showing GCG + cAMP expression in the pancreas, with GCG in green, cAMP in red, and cell nuclei in blue. Bars = 20 μm; G: Pancreatic GCG+ IOD; H: CAMP IOD in pancreatic α cells. All the data are presented as the mean ± SE. aP < 0.01 vs diabetic mice; bP < 0.01 vs diabetic mice with a single hypoglycemic episode (DH1); dP < 0.05 vs DH1 group; DM: Diabetic mice; DH1: Diabetic mice with a single hypoglycemic episode; DH5: Diabetic mice with five hypoglycaemic episodes; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; IOD: Integrated optical density.
- Citation: Jin FX, Wang Y, Li MN, Li RJ, Guo JT. Intestinal glucagon-like peptide-1: A new player associated with impaired counterregulatory responses to hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetic mice. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(8): 1764-1777
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i8/1764.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i8.1764