Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2024; 15(7): 1537-1550
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i7.1537
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i7.1537
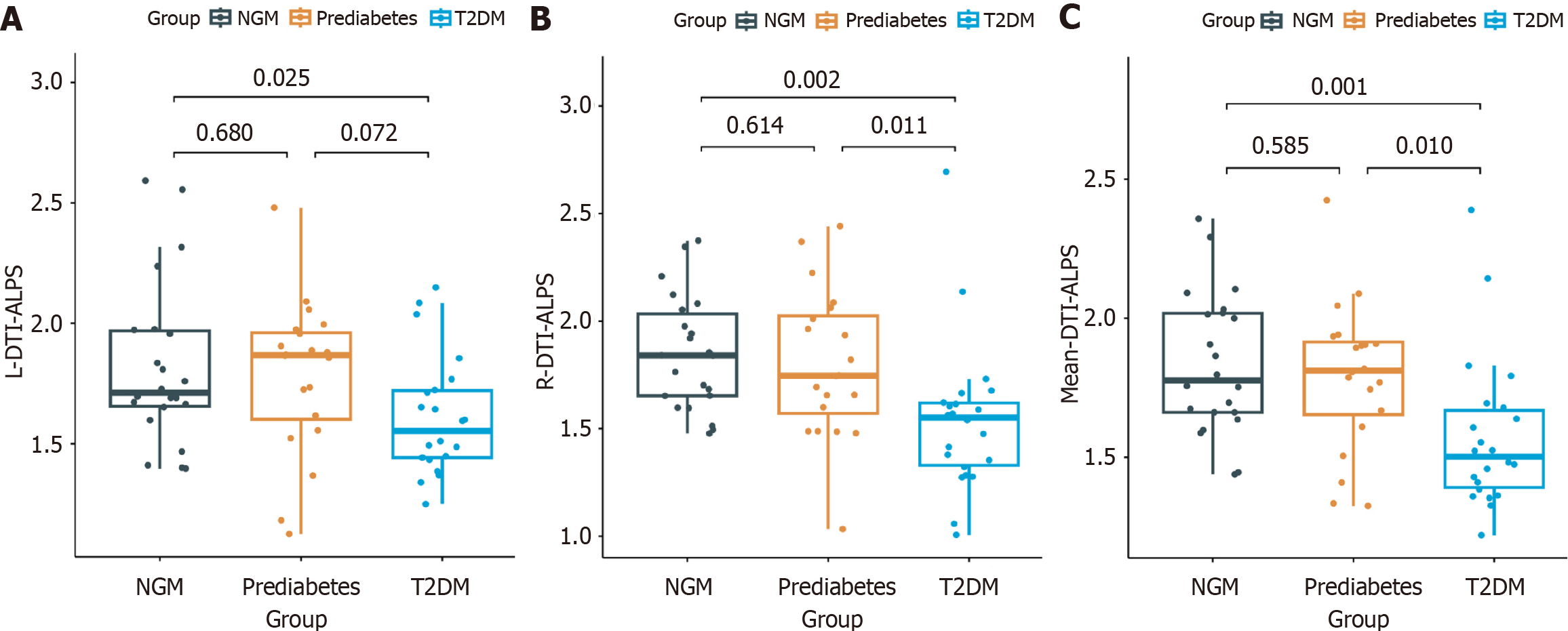
Figure 2 The left-side\right-side\mean diffusion tensor image analysis method along the perivascular space index was evaluated.
A: The diffusion tensor image analysis method along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) index of the left-side cerebral hemisphere in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) was significantly lower than in the normal glucose metabolism (NGM) group; B: The DTI-ALPS index of the right cerebral hemisphere in patients with T2DM was significantly lower than that in the prediabetes group and the NGM group; C: The mean DTI-ALPS index of both cerebral hemispheres in patients with T2DM was significantly higher in the prediabetes and NGM groups. T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; NGM: Normal glucose metabolism; DTI-ALPS: Diffusion tensor image analysis method along the perivascular space; L-DTI-ALPS: Diffusion tensor image analysis method along the perivascular space index of the left cerebral hemisphere in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus; R-DTI-ALPS: Diffusion tensor image analysis method along the perivascular space index of the right cerebral hemisphere of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus; Mean-DTI-ALPS: Mean Diffusion tensor image analysis method along the perivascular space index in both cerebral hemispheres.
- Citation: Tian B, Zhao C, Liang JL, Zhang HT, Xu YF, Zheng HL, Zhou J, Gong JN, Lu ST, Zeng ZS. Glymphatic function and its influencing factors in different glucose metabolism states. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(7): 1537-1550
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i7/1537.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i7.1537