Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2024; 15(6): 1162-1177
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1162
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1162
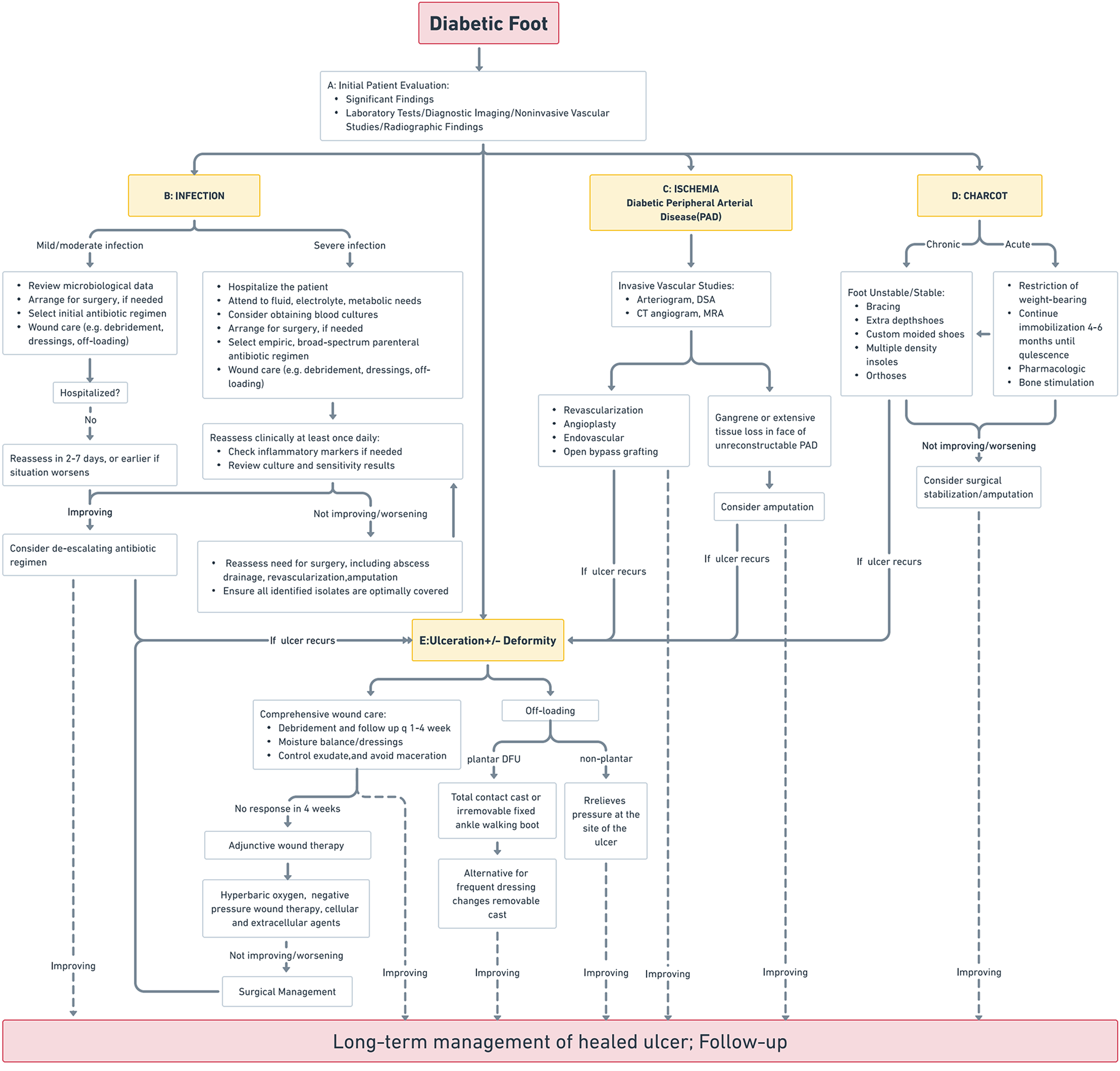
Figure 1 Standard clinical protocols for diabetic foot.
This figure illustrates a detailed algorithm for managing diabetic foot complications, with a focus on infection, ischemia resulting from peripheral arterial disease, and Charcot neuroarthropathy. A: Initial evaluation: Incorporates diagnostic testing and imaging to guide therapeutic decisions; B: Infection management: Encompasses a spectrum from antibiotic therapy and localized wound care to hospitalization for advanced cases. Surgical intervention is considered for non-responsive infections; C: Ischemia treatment: Strategies include revascularization and angioplasty, with amputation reserved for critical cases; D: Charcot neuroarthropathy management: Ranges from conservative orthopedic approaches to surgical correction, based on disease progression and treatment response; E: Ulceration and deformity management: Emphasizes comprehensive wound care, off-loading techniques, and surgical options when necessary. The decision-making process within the algorithm is dynamic, adjusting based on the ulcer’s response to treatment and incorporating adjunctive therapies such as hyperbaric oxygen or cellular and tissue-based products where appropriate.
- Citation: Tseng SL, Kang L, Li ZJ, Wang LQ, Li ZM, Li TH, Xiang JY, Huang JZ, Yu NZ, Long X. Adipose-derived stem cells in diabetic foot care: Bridging clinical trials and practical application. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(6): 1162-1177
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i6/1162.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1162