Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2024; 15(5): 958-976
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.958
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.958
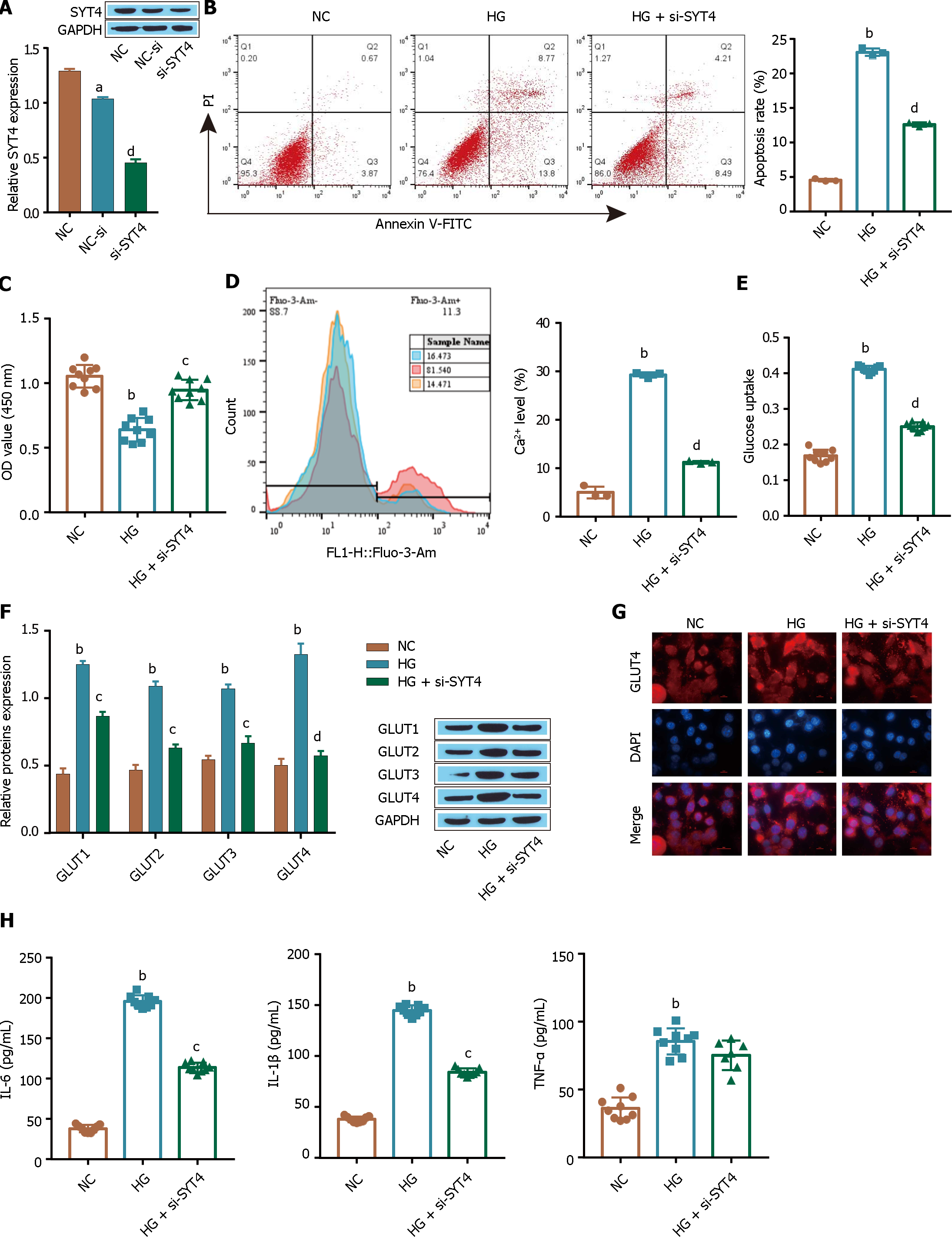
Figure 2 Synaptotagmins 4 promotes high glucose-induced cellular glucose uptake by ARPE-19 cells.
A: The expression of synaptotagmins 4 (SYT4) was detected via Western blot; B: Apoptosis was observed by flow cytometry; C: A Cell Counting Kit-8 assay was used to determine cell viability; D: Flow cytometry was used to determine intracellular Ca2+ levels; E: Glucose uptake levels were determined; F: Western blot was used to detect the glucose transporter; G: Immunofluorescence analysis was used to examine the extent of GLUT1 membrane translocation; H: The levels of inflammatory cytokines [tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6] were measured via ELISA. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001, vs the NC group; cP < 0.01, dP < 0.01 vs the NC group, HG group. SYT: Synaptotagmins; GLUT1: Glucose transporter-1; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Xu H, Zhang LB, Luo YY, Wang L, Zhang YP, Chen PQ, Ba XY, Han J, Luo H. Synaptotagmins family affect glucose transport in retinal pigment epithelial cells through their ubiquitination-mediated degradation and glucose transporter-1 regulation. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(5): 958-976
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i5/958.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.958