Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2024; 15(5): 898-913
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.898
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.898
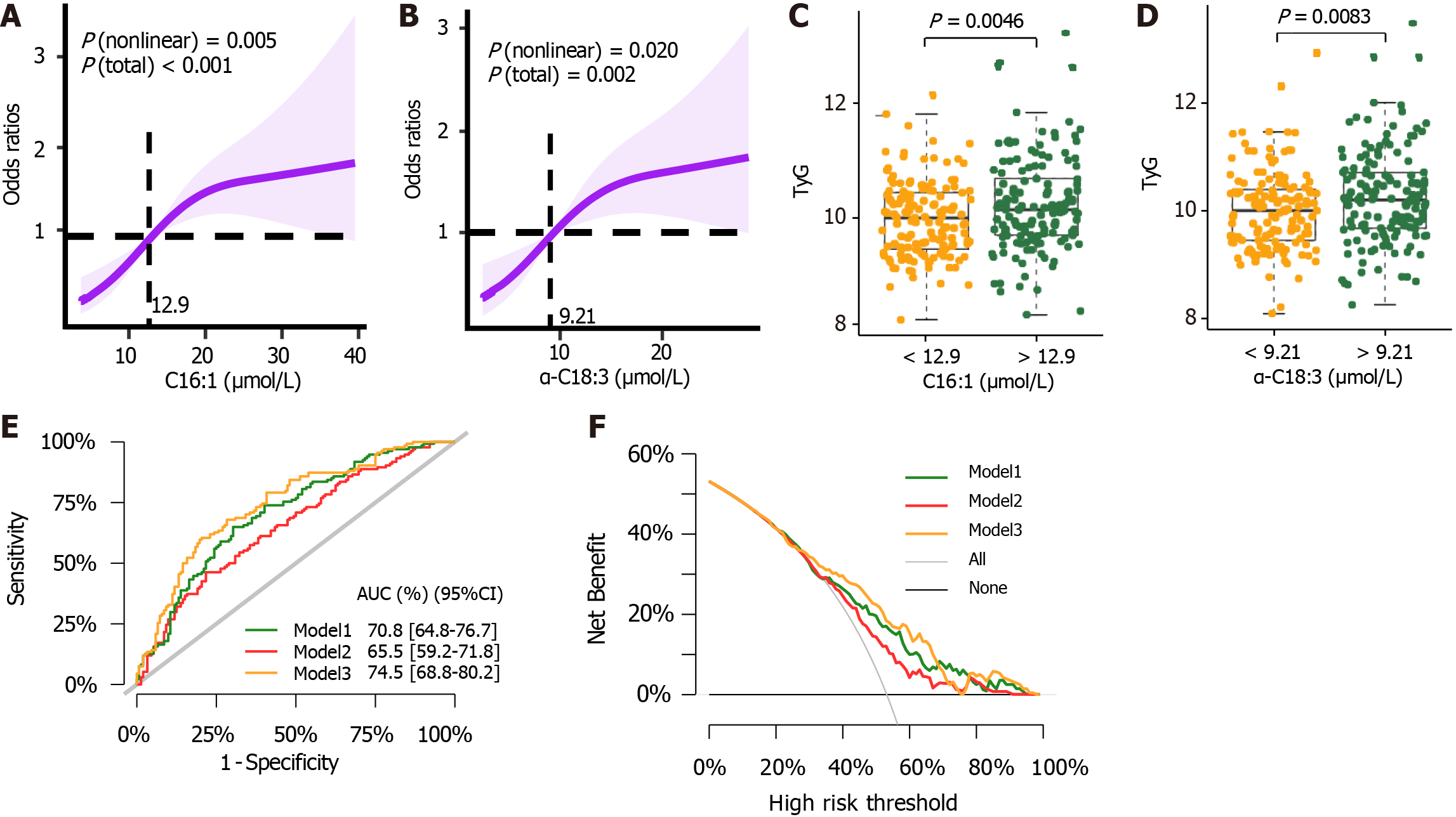
Figure 4 Logistic regression risk prediction model about non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
A: Odds ratio (OR) was represented in restricted cubic splines (RCS) nested showing association of palmitoleic acid (C16:1) level on a continuous scale and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM); B: OR was represented in RCS nested showing association of alpha-octadecatrienoic acid (α-C18:3) level on a continuous scale and NAFLD in T2DM. Shaded areas represent 95% confidence interval (95%CI). 12.9 and 9.21 μmol/L were set as the reference values for C16:1 and α-C18:3 respectively; C: C16:1 was analyzed for their relationship with Triglyceride glucose index (TyG) by threshold; D: α-C18:3 was analyzed for their relationship with TyG by threshold. The statistical comparison was performed by the Wilcoxon test (statistically significant: P < 0.05); E: Comparison of three NAFLD predictive model assessments of the 95%CI of their area under the curve values; F: Comparison of model performance from Decision Curve analysis. Model 1 consists of C16:1, α-C18:3, eicosapentaenoic acid, ω-3 docosapentaenoic acid, γ-linolenic acid. Model 2 consists of sex, age, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, duration of diabetes, TyG, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, glycosylated hemoglobin, fasting c-peptide, and c-peptide 2 h postprandial. Model 3 was constructed by the factors of model 2 and model 1 together. C16:1: Association of palmitoleic acid; α-C18:3: Alpha-octadecatrienoic acid; 95%CI: 95% confidence interval; AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Feng SS, Wang SJ, Guo L, Ma PP, Ye XL, Pan ML, Hang B, Mao JH, Snijders AM, Lu YB, Ding DF. Serum bile acid and unsaturated fatty acid profiles of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetic patients. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(5): 898-913
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i5/898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.898