Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2024; 15(5): 867-875
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.867
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.867
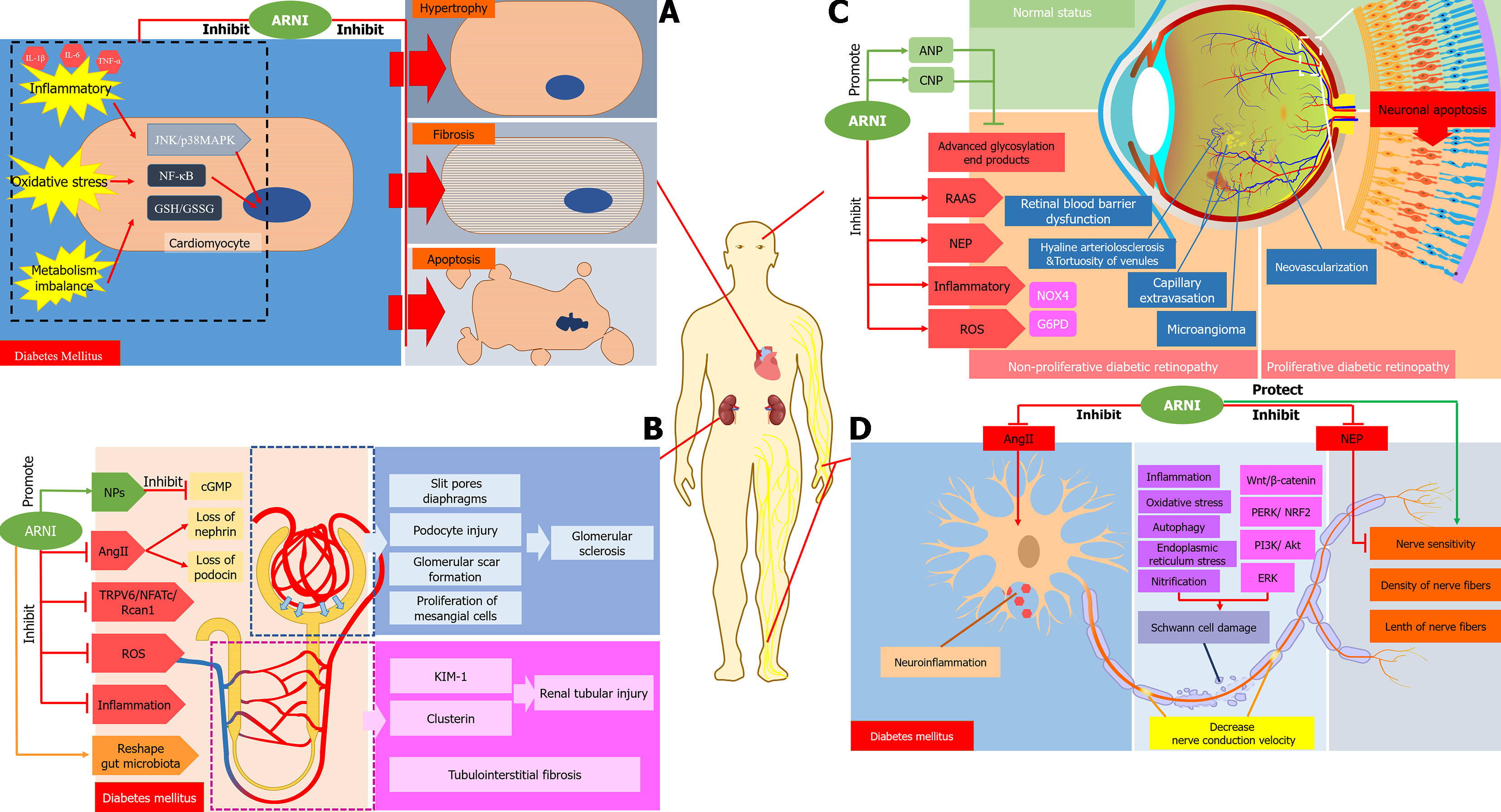
Figure 2 Role and mechanisms of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor in diabetic complications.
A: Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) has protective effects on diabetic myocardial tissue through anti-apoptosis, anti-fibrosis, anti-inflammation, anti-oxidative stress activities and improving metabolism; B: ARNI reduces inflammation, Ang II, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits the transient receptor potential-6/NFATc/Rcan1 pathway, which may improve podocyte integrity, protects glomerular and renal tubular function and structure; C: ARNI alleviates diabetic retinopathy by the inhibiting renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, ROS and inflammatory response and simultaneously increasing the protective effects of atrial natriuretic peptide and C-type natriuretic peptide; D: ARNI delays the development of diabetic peripheral neuropathy by reducing Ang II and inhibiting the effect of neprilysin, improving nerve conduction velocity and sensitivity and protecting Schwann cells. ARNI: Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; GSH: Glutathione; GSSG: Glutathione/glutathione disulfide; NPs: Natriuretic peptide system; TRPV6: Transient receptor potential-6; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; KIM-1: Kidney injury molecule-1; ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; CNP: C-type natriuretic peptide; RAAS: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; NEP: Neprilysin; NOX4: NADPH oxidases 4; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; G6PD: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; NRF2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; p38MAPK: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; PERK: Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
- Citation: Liu Y, Lu CY, Zheng Y, Zhang YM, Qian LL, Li KL, Tse G, Wang RX, Liu T. Role of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor in diabetic complications. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(5): 867-875
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i5/867.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.867