Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2024; 15(5): 853-866
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.853
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.853
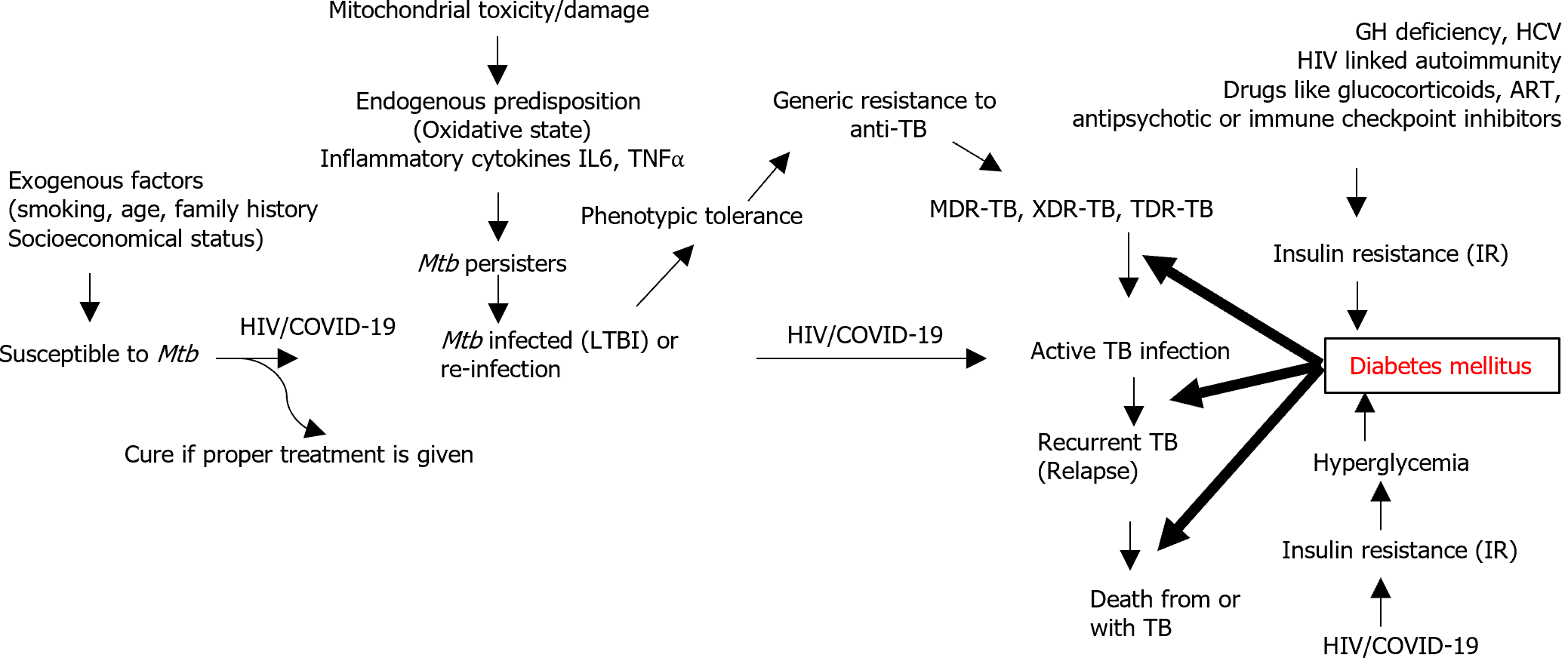
Figure 1 Pathophysiological relationships between tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus and impacts of exogenous and endogenous factors.
Both tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus show a bidirectional relationship at various points as depicted, which are affected by exogenous and endogenous factors. GH: Growth hormone; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; ART: Antiretroviral therapy; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; PDL-1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; IR: Insulin resistance; TB: Tuberculosis; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; MDR: Multi-drug resistant; XDR: Extreme drug resistance; TDR: Total drug-resistance; IL: Interleukin; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
- Citation: Al-Bari MAA, Peake N, Eid N. Tuberculosis-diabetes comorbidities: Mechanistic insights for clinical considerations and treatment challenges. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(5): 853-866
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i5/853.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i5.853