Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2024; 15(4): 697-711
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.697
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.697
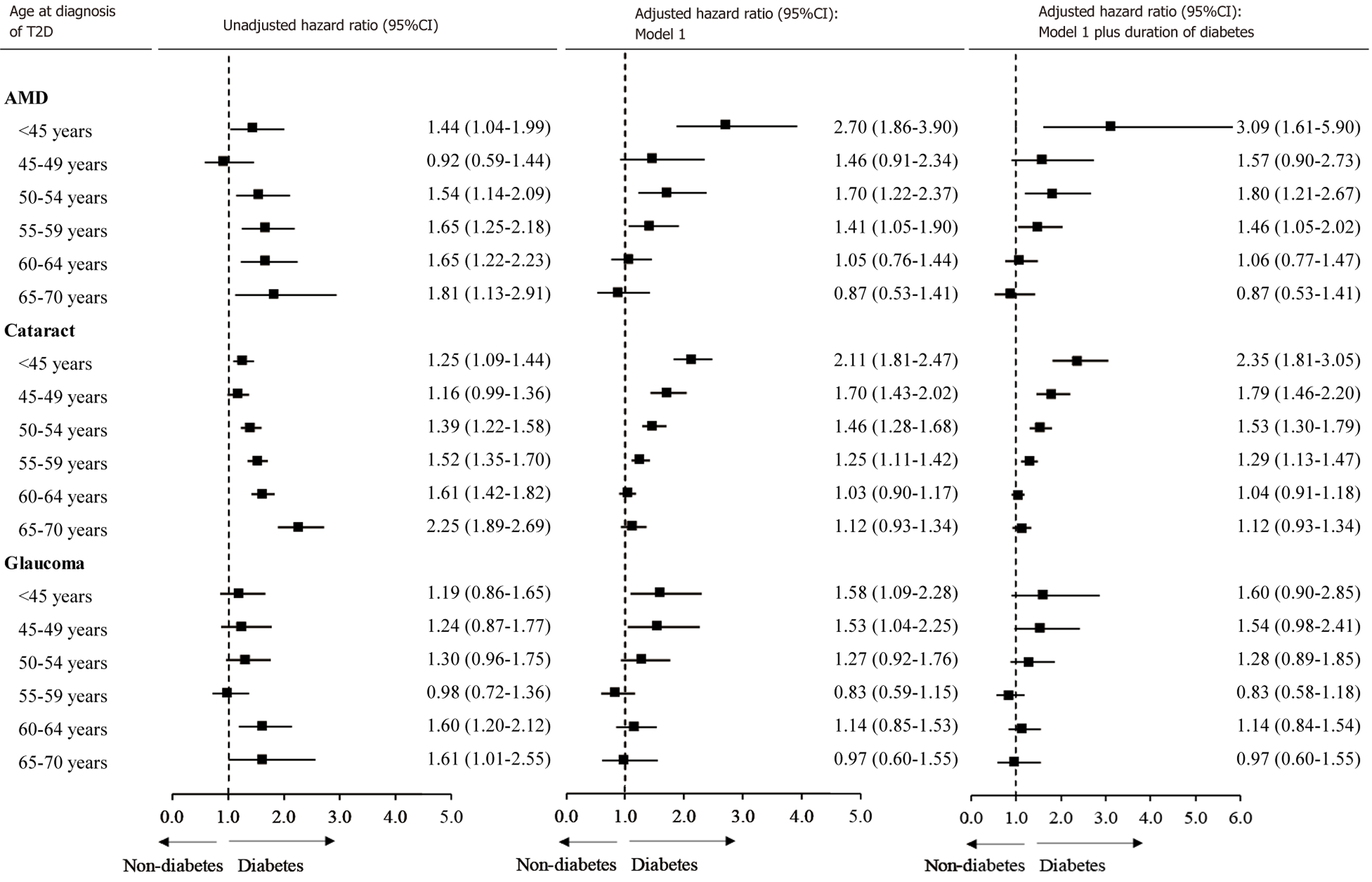
Figure 5 Risk for ocular conditions associated with age at diagnosis of diabetes with the same reference.
Sensitivity analysis was conducted to randomly select controls for each individual with type 2 diabetes with all diabetic patients as a whole. Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to estimate hazard ratios for ocular conditions associated with age at diagnosis of diabetes with controls as the reference for each group of diabetes diagnosed age. The multivariable model was adjusted for age, gender, ethnicity, income, education, alcohol consumption, physical activity, sleep duration, smoking, body mass index, depression, hypertension, heart disease, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglyceride, and glycated haemoglobin. Central squares of each horizontal line represent the hazard ratio for each subgroup. Horizontal lines indicate the range of the 95%CI. The vertical dash lines indicate the hazard ratio of 1.0. T2D: Type 2 diabetes; AMD: Age-related macular degeneration.
- Citation: Ye ST, Shang XW, Huang Y, Zhu S, Zhu ZT, Zhang XL, Wang W, Tang SL, Ge ZY, Yang XH, He MG. Association of age at diagnosis of diabetes with subsequent risk of age-related ocular diseases and vision acuity. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(4): 697-711
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i4/697.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.697