Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2024; 15(3): 519-529
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.519
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.519
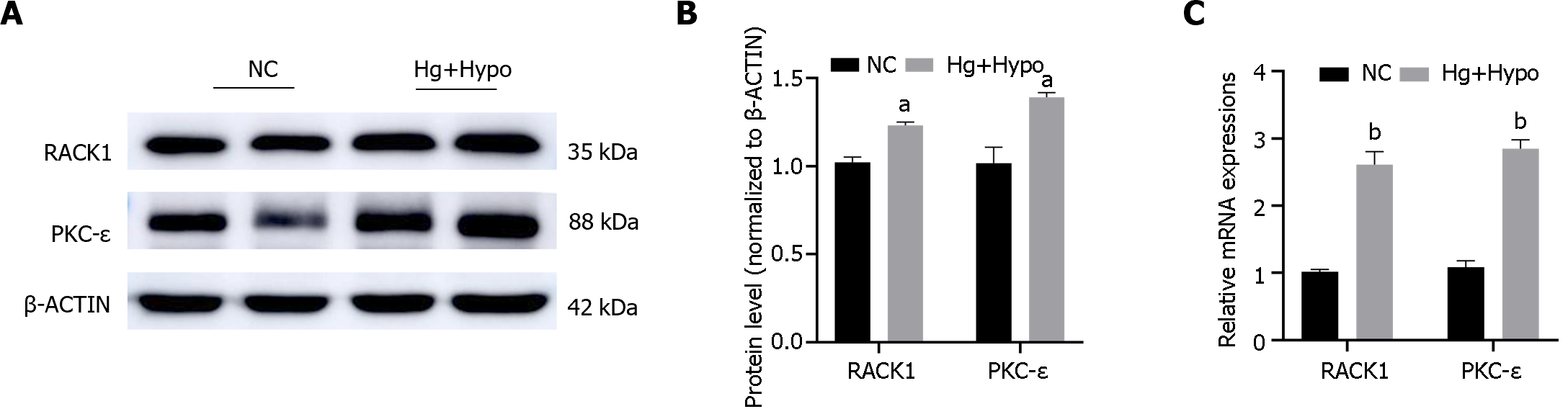
Figure 4 High glucose combined with hypoxia up-regulated transcription and increased protein levels of receptor for activated C kinase 1 and protein kinase C-ε in adult retinal pigment epithelium cell line-19 cells.
A and B: The protein levels of receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) and protein kinase C-ε (PKC- ε) in the adult retinal pigment epithelium cell line-19 (ARPE-19) cells of normal control and high glucose combined with hypoxia; C: The ratio of mRNA of RACK1 and PKC- ε in ARPE-19 cells. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs control group. bP < 0.01 vs control group. NC: Normal control; Hg + Hypo: High glucose combined with hypoxia; RACK1: Receptor for activated C kinase 1; PKC- ε: Protein kinase C-ε.
- Citation: Tan J, Xiao A, Yang L, Tao YL, Shao Y, Zhou Q. Diabetes and high-glucose could upregulate the expression of receptor for activated C kinase 1 in retina. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(3): 519-529
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i3/519.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.519