Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2024; 15(3): 488-501
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.488
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.488
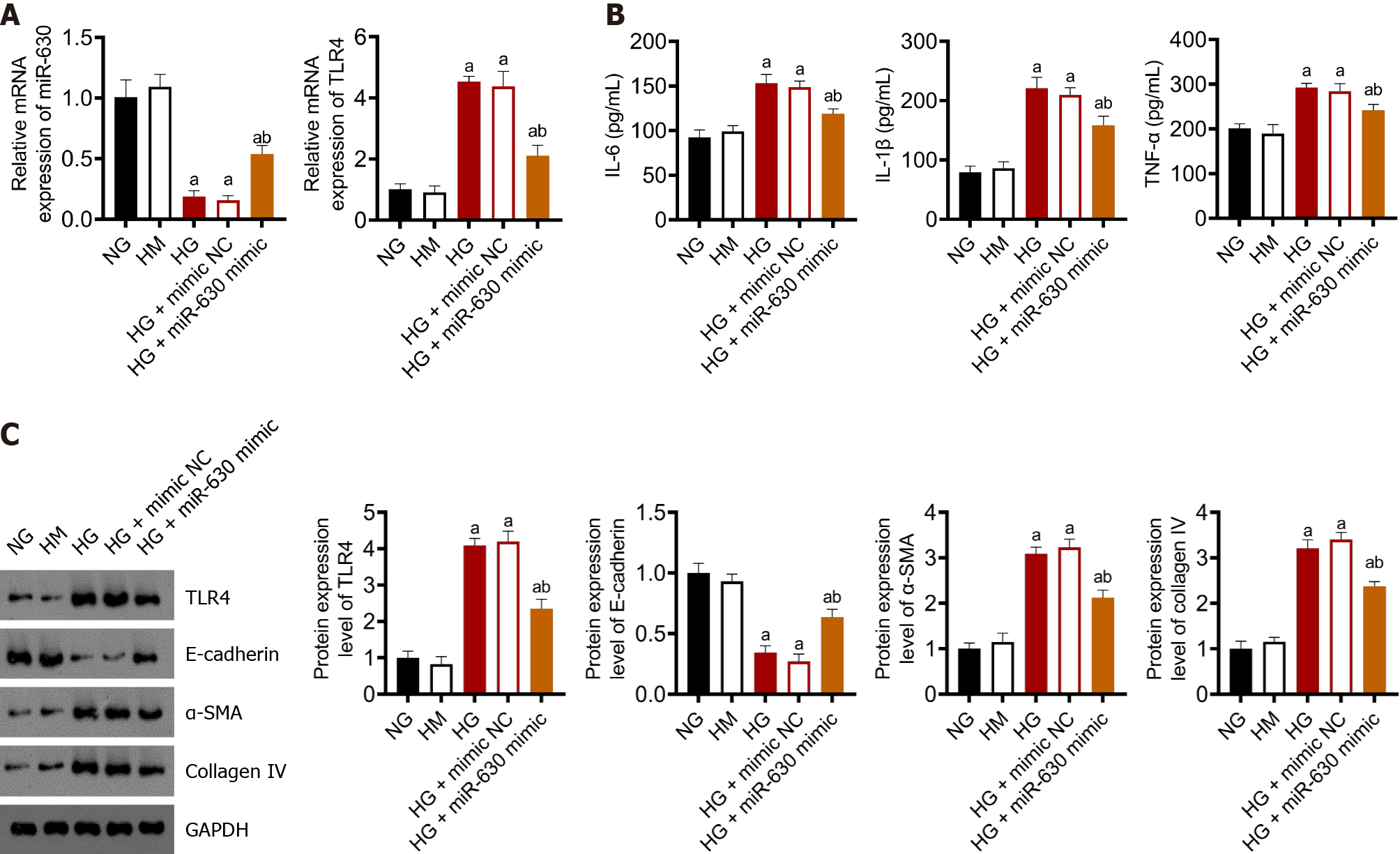
Figure 2 Overexpression of miR-630 inhibits renal tubular epithelial cell damage induced by high glucose in vitro.
A: Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction detection of miR-630 and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression in rat renal tubular epithelial cells in a high glucose environment (NRK-52E); B: Detection of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 expression in rat renal tubular epithelial cells (NRK-52e) under a high glucose environment by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; C: Western blot detection of NRK-52E TLR4 in rats under a high glucose environment α-smooth muscle actin and collagen IV protein expression. Data are presented as mean ± SD, aP < 0.01 vs normal glucose, and bP < 0.01 vs high glucose + mimic normal glucose. NG: Normal glucose, 5.6 mmol/L; HG: High glucose, 20 mmol/L; HM: High mannitol (5.6 mmol/L glucose + 14.4 mmol/L mannitol); TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Wu QS, Zheng DN, Ji C, Qian H, Jin J, He Q. MicroRNA-630 alleviates inflammatory reactions in rats with diabetic kidney disease by targeting toll-like receptor 4. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(3): 488-501
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i3/488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.488